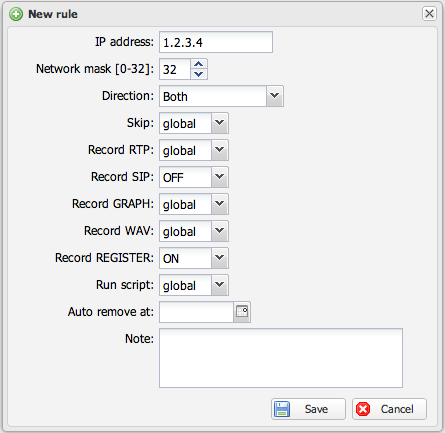
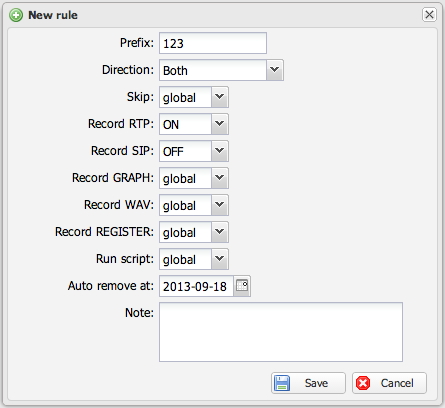
Capture rules
Capture rules enable selective recording of calls based on IP addresses or phone numbers. By default, RTP packets may not be fully saved, but rules can enable full RTP recording, call graphs, or SIP signaling capture for specific calls. Rules can also trigger external shell scripts.
How Capture Rules Work
The sniffer loads capture rules on startup and supports hot-reloading without service restart. Changes in the GUI are not automatically applied - click the green reload sniffer button to apply them.
Limitations
⚠️ Warning: Understand what capture rules do NOT support before planning your recording strategy.
| Requirement | Supported | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| SIP header-based filtering | NO | Use filter directive in voipmonitor.conf with BPF syntax
|
| Source AND Destination combinations | NO | IP rules use OR logic only. Use filter directive for AND logic
|
| IP direction matching | YES | Rules support source, destination, or both directions |
| Phone number direction | YES | Rules support caller, called, or both directions |
Rule Options
3-State Options
| State | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| GLOBAL | Inherits from global sniffer config | Enable SIP REGISTER for specific IPs without overriding RTP settings |
| ON | Explicitly enables the option | Force recording for matched calls |
| OFF | Explicitly disables the option | Disable recording for matched calls |
RTP Options (4 States)
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| GLOBAL | Inherits from savertp in voipmonitor.conf
|
| ON | Save full RTP audio payload |
| OFF | Discard RTP entirely |
| HEADER | Save only RTP headers - captures quality metrics (MOS, jitter) without audio (up to 90% storage reduction) |
Example: Set global default to headers, then record full audio for specific IPs:
# voipmonitor.conf
savertp = header
Then create a GUI capture rule for needed IP(s) with RTP option set to ON.
Special Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Skip | Ignores matched calls entirely - no CDR, no files, no analysis. Only works if IP/number appears in SIP signalling (not RTP-only traffic). For RTP-only exclusion, use the filter directive.
|
| Auto remove at | Deletes the rule on specified date. Note: Permanently deletes the rule (not deactivates), and deletion is NOT logged in Audit Log. |
Script Integration
Rules can trigger external shell scripts via filtercommand option. See Sniffer Configuration.
Storage Options
Secondary Spooldir (spooldir_2)
Route PCAP files for specific traffic to a secondary storage with separate retention policies.
Use Cases: Legal holds, VIP customers, regulatory requirements.
# voipmonitor.conf
spooldir_2 = /var/spool/voipmonitor2
maxpoolsize_2 = 1000G
maxpooldays_2 = 365
Then create a capture rule and enable Store pcaps to second spooldir.
ℹ️ Note: spooldir_2 is NOT automatic overflow. When primary fills up, cleanspool deletes oldest files - it does NOT write to spooldir_2.
On-Demand Audio (spooldir_rtp)
Store RTP packets separately for on-demand GUI audio playback:
# voipmonitor.conf
spooldir_rtp = /path/to/fast/storage
Create a capture rule with RTP option set to ON to save to this location.
GUI Usage
- Navigate to Control Panel (Dashboard)
- Click Capture Rules section
- Create rules using IP or TEL number filters
- Click green reload sniffer button to apply
Selective OPTIONS Recording
Save SIP OPTIONS packets for specific IPs only:
# voipmonitor.conf - disable global OPTIONS saving
save-sip-options = no
Then create an IP-based capture rule with Record OPTIONS enabled. See SIP_OPTIONS/SUBSCRIBE/NOTIFY for details.
Use Cases
PCI DSS: Selective DTMF Recording
Disable DTMF globally but enable for troubleshooting specific traffic:
# voipmonitor.conf
dtmf2db = no
Create a capture rule for specific IP/number with record DTMF set to ON.
💡 Tip: Use Auto remove at to limit rule lifetime. Keep scope narrow (specific IP/number) to minimize data retention.
Compliance Audit Limitations
| Requirement | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic rule expiration | Supported | Auto remove at option; also autoexpire timeout in user settings |
| Track who modified rules | Partial | Audit Log shows timestamp/IP only, NOT user or specific changes |
| Temporary deactivation | NOT Supported | Rules can only be active or deleted |
| Log auto-removal | NOT Supported | Expiration deletions not logged |
Inspection methods for DTMF-enabled rules:
- Database:
SELECT ip, INET_NTOA(ip), direction FROM filter_ip WHERE dtmf=1; - Manager API:
echo 'crules_print' | nc SENSOR_IP 5029
ℹ️ Note: New in 2026.1: The table above has been updated:
- Temporary deactivation is now Supported via auto-disable feature (per-rule or global setting)
- Log auto-removal is now Supported - automatic disable/removal events are recorded in Audit Log
Database Management
For automation or bulk operations, manipulate rules directly in MySQL.
Tables
| Table | Purpose |
|---|---|
filter_ip |
IP address/subnet rules |
filter_telnum |
Telephone number prefix rules |
IP-Based Rule Example
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ip |
INT UNSIGNED | IP via INET_ATON()
|
mask |
TINYINT | CIDR notation (e.g., 24)
|
direction |
TINYINT | 0=both, 1=source, 2=destination |
rtp |
TINYINT | 1=SAVE, 2=DISCARD, 3=header only |
-- Force RTP for 1.2.3.0/24 network
INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_ip (ip, mask, direction, rtp)
VALUES (INET_ATON('1.2.3.0'), 24, 0, 1);
Telephone Number Rule Example
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
prefix |
VARCHAR | Number prefix to match |
fixed_len |
TINYINT | 0=prefix match |
direction |
TINYINT | 0=both, 1=caller, 2=called |
rtp |
TINYINT | 1=SAVE, 2=DISCARD, 3=header only |
-- Force RTP when called number starts with 98765
INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_telnum (prefix, fixed_len, direction, rtp)
VALUES ('98765', 0, 2, 1);
Reloading Rules
Rules do NOT take effect until reloaded.
Method 1: GUI (Recommended)
Click green reload sniffer button in Control Panel.
Method 2: Manager API
echo 'reload' | nc SENSOR_IP 5029
Method 3: Server API (Client/Server Mode)
For sensors behind NAT using distributed architecture:
# Get sensor ID
echo 'list_active_clients' | nc SERVER_IP 5029
# Output: {"count":1,"services":[{"ip":"127.0.0.1","port":54137,"sensor_id":114}]}
# Send reload via Server API (port 60024)
echo '{"type_connection":"gui_command","sensor_id":114,"command":"reload"}' | nc SERVER_IP 60024
Troubleshooting
Audio Recording Despite savertp=header
Cause: Capture rules with RTP=ON override global settings.
Solution:
- Check GUI > Control Panel > Capture Rules for rules with recordRTP = ON
- Set to OFF or GLOBAL to inherit from config
- Click reload sniffer
Rules Not Applied
Step 1: Test connectivity
echo 'getversion' | nc SENSOR_IP 5029
| Result | Action |
|---|---|
| Version string | Proceed with reload |
| Timeout | Check firewall for port 5029/TCP |
| Connection refused | Check sensor service: systemctl status voipmonitor
|
Step 2: Workaround if reload fails
systemctl restart voipmonitor
Cleaning Up Old Recordings After Rule Change
New rules only affect future calls. To clean up existing recordings:
- Go to Settings > Custom Autocleaning
- Create rule with time filter (e.g., "older than 1 day")
- Set Common Filter matching same IP/phone number
- Run once, then remove the autocleaning rule
See Data Cleaning - Custom Autocleaning.
Verify Rules Are Active
# Check logs for reload confirmation
journalctl -u voipmonitor | grep -i reload
Add send_manager_cmd crules_print command to verify active capture rules
# List active capture rules from sensor's perspective (encrypted connection)
php php/run.php send_manager_cmd -s <sensor_id> -c crules_print
ℹ️ Note: The crules_print command prints capture rules as loaded by the sensor. Rules update automatically 1 minute after the last change or via the reload sniffer button, but the listing may only update after the first SIP packet arrives.
# Alternative: direct Manager API command (requires encrypted connection disabled OR Unix socket)
echo 'crules_print' | nc -U /tmp/vm_manager_socket
Alternatives to Capture Rules
Filter Directive (BPF)
Use filter in voipmonitor.conf when:
- IP only appears in RTP packets (not SIP signalling)
- You need IP pair combinations with AND logic
- Skip option affects unintended calls
# Exclude specific IP
filter = not host 187.60.50.46
# Exclude subnet
filter = not net 10.0.0.0/8
# Capture only traffic between specific IP pair (AND logic)
filter = host 192.168.1.10 and host 10.0.0.5
# Multiple pairs with OR
filter = (host 192.168.1.10 and host 10.0.0.5) or (host 192.168.1.10 and host 10.0.0.6)
⚠️ Warning: filter uses BPF which adds CPU load. Requires service restart. For best performance, filter at network level (router/firewall).
See Sniffer Configuration - filter.
See Also
- Sniffer_configuration - Full configuration reference
- Data_Cleaning - Storage and retention management
- SIP_OPTIONS/SUBSCRIBE/NOTIFY - OPTIONS recording details
- Sniffer_distributed_architecture - Client/server mode
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: VoIPmonitor capture rules enable selective call recording based on IP addresses or phone numbers. Key features: 3-state options (GLOBAL/ON/OFF), RTP 4-state (adds HEADER for metadata-only), Skip (ignore calls), Auto remove at (time-limited rules). Critical limitations: SIP header filtering NOT supported, IP combinations use OR logic only (no AND). For complex filtering, use filter directive with BPF. Storage options: spooldir_2 for separate retention (legal holds), spooldir_rtp for on-demand GUI audio. Rules stored in filter_ip/filter_telnum tables. Reload via GUI button, Manager API (echo 'reload' | nc IP 5029), or Server API for client/server mode. Common issue: Audio recording despite savertp=header caused by capture rules with RTP=ON overriding global settings. Compliance: auto-expiration supported, but Audit Log shows only timestamp/IP (not user or specific changes), auto-removal not logged.
Keywords: capture rules, selective recording, RTP packets, filter_ip, filter_telnum, INET_ATON, sniffer reload, skip calls, auto-remove, manager api, port 5029, filter directive, BPF, PCI DSS, DTMF, dtmf2db, crules_print, SIP OPTIONS, spooldir_2, legal hold, savertp override, spooldir_rtp
Key Questions:
- How do capture rules work in VoIPmonitor?
- What are the limitations of capture rules (SIP headers, IP AND logic)?
- How do I reload rules without restarting the sniffer?
- Why is audio recorded despite savertp=header?
- What does the Skip option do?
- How do I use spooldir_2 for legal holds?
- How can I use capture rules for PCI DSS compliance with DTMF?
- How do I inspect which rules have DTMF enabled?
- How do I reload rules on a remote sensor behind NAT?
- What is the filter directive alternative for complex IP filtering?