Glossary: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Glossary of VoIP & Monitoring Terms}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Glossary of VoIP & Monitoring Terms}} | ||
''' | '''Quick reference for VoIP quality metrics and monitoring concepts used in VoIPmonitor.''' | ||
== | == Network Quality Metrics == | ||
=== Packet Loss === | === Packet Loss === | ||
Lost data packets cause audible gaps, clicks, or dropouts. Common causes: congestion, faulty hardware, misconfiguration. | |||
'''VoIPmonitor approach:''' Records loss distribution (how many consecutive packets lost in various intervals) rather than just average percentage. This matters because 2% random loss is far less noticeable than a 2-second burst of 100% loss. | |||
=== Packet Delay Variation (PDV) | === Packet Delay Variation (PDV) / Jitter === | ||
Variation in packet arrival times from expected intervals. High jitter = erratic packet bursts = degraded quality even without packet loss. | |||
'''VoIPmonitor approach:''' Measures packets exceeding delay thresholds: | |||
* 50–70ms, 70–90ms, 90–120ms, 120–150ms, 150–300ms, >300ms | |||
* 50–70ms | |||
{{Note|1='''Constant jitter values''' (same value throughout call) indicate clock mismatch in device, not network issues. '''Zero jitter with large initial delay''' = one-time buffering spike, not ongoing jitter.}} | |||
=== Post-Dial Delay (PDD) === | === Post-Dial Delay (PDD) === | ||
Time from last digit dialed to first feedback (ringback/busy tone). Long PDD causes users to hang up prematurely. | |||
== Mechanisms | == Mitigation Mechanisms == | ||
=== Jitter Buffer | === Jitter Buffer === | ||
Temporary storage at receiving end that delays and reorders packets for smooth playback. Types: | |||
* '''Fixed:''' Constant buffer size | |||
* '''Adaptive:''' Dynamically adjusts based on network conditions | |||
=== Packet Loss Concealment (PLC) === | === Packet Loss Concealment (PLC) === | ||
Masks lost packets since retransmission is not feasible in real-time voice: | |||
= | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |||
! Technique !! Description | |||
|- | |||
| Zero Insertion || Replace with silence (crudest method) | |||
|- | |||
| Waveform Substitution || Repeat last known frame (common, per G.711 Appendix I) | |||
|- | |||
| Model-Based || Interpolate missing audio using speech models (best quality) | |||
|} | |||
== Voice Quality | == Voice Quality Metrics == | ||
=== Mean Opinion Score (MOS) === | === Mean Opinion Score (MOS) === | ||
MOS is a standardized numerical rating of perceived voice quality, ranging from 1 (bad) to 5 (excellent). Originally a subjective test where human listeners would rate call quality, it is now typically calculated objectively using algorithms like the one defined in the ITU-T P.862 (PESQ) standard. | MOS is a standardized numerical rating of perceived voice quality, ranging from 1 (bad) to 5 (excellent). Originally a subjective test where human listeners would rate call quality, it is now typically calculated objectively using algorithms like the one defined in the ITU-T P.862 (PESQ) standard. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! MOS !! Quality !! Impairment | ! MOS !! Quality !! Impairment | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Codec baseline scores:''' | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Codec !! | ! Codec !! Bitrate !! Typical MOS | ||
|- | |- | ||
| G.711 | | G.711 || 64 kbit/s || 4.1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| iLBC || 15.2 || 4.14 | | iLBC || 15.2 kbit/s || 4.14 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| AMR || 12.2 || 4.14 | | AMR || 12.2 kbit/s || 4.14 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| G.729 || 8 || 3.92 | | G.729 || 8 kbit/s || 3.92 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| G.723.1 | | G.723.1 || 6.3 kbit/s || 3.9 | ||
|} | |||
==== VoIPmonitor MOS Calculation ==== | |||
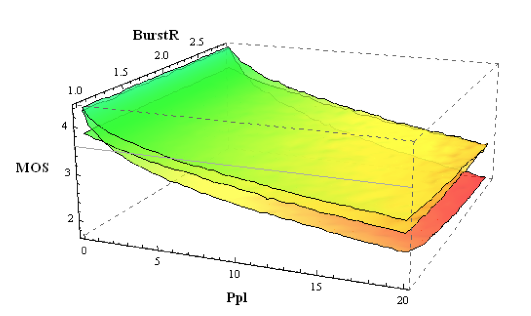
VoIPmonitor calculates '''parametric MOS''' from network metrics (packet loss, PDV), not the audio signal. It simulates jitter buffer performance: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | ! Score !! Jitter Buffer Model !! Use Case | ||
|- | |||
| '''MOS F1''' || Fixed 50ms || Very sensitive to jitter | |||
|- | |||
| '''MOS F2''' || Fixed 200ms || Moderate tolerance | |||
|- | |||
| '''MOS adapt''' || Adaptive up to 500ms || Real-world endpoint simulation | |||
|} | |} | ||
Default calculation uses G.711 codec with PLC for consistent cross-call comparison. | |||
[[File:mos.png|VoIPmonitor calculates MOS based on simulated packet loss and PDV, using a pre-calculated surface for G.711 with PLC.]] | [[File:mos.png|VoIPmonitor calculates MOS based on simulated packet loss and PDV, using a pre-calculated surface for G.711 with PLC.]] | ||
=== R-Factor === | |||
{{Warning|1='''VoIPmonitor does NOT calculate R-Factor.''' R-Factor (ITU-T G.107 E-Model, 0-100 scale) is redundant because MOS provides equivalent information with direct mathematical correlation.}} | |||
'''Recommended approach instead:''' | |||
* Track '''MOS percentiles''' (%95, %99) not averages | |||
* Monitor '''changes over time''' against historical baselines | |||
* Use VoIPmonitor's aggregation by source IP/number | |||
=== RTCP | === RTCP === | ||
RTP Control Protocol provides endpoint-reported statistics: transmitted/lost packets, jitter, round-trip delay. VoIPmonitor parses RTCP reports for alternative view of call quality. | |||
== | == Carrier-Grade Metrics == | ||
=== | === ASR (Answer-Seizure Ratio) === | ||
Percentage of answered calls from total attempts (ITU E.411): | |||
=== Average Call Duration | <code>ASR = (Answered Calls / Total Seizures) × 100</code> | ||
Low ASR can indicate network problems but is also affected by user behavior (busy, no answer). | |||
=== NER (Network Effectiveness Ratio) === | |||
Like ASR but measures only network capability—calls reaching destination but rejected by user (busy, no answer) count as "successful." Configure which SIP codes are successful in Settings. | |||
=== ACD (Average Call Duration) === | |||
Average length of answered calls. Low ACD combined with low ASR often indicates quality problems (users hanging up due to poor audio). | |||
== Statistical Concepts == | == Statistical Concepts == | ||
=== Percentiles === | === Percentiles === | ||
Value below which a given percentage of observations falls. | |||
'''Example:''' <code>MOS %95 = 3.2</code> means 5% of calls had MOS of 3.2 or worse. More useful than averages for identifying systemic problems. | |||
== See Also == | |||
* [[Comprehensive_Guide_to_VoIP_Voice_Quality]] - Detailed voice quality analysis | |||
* [[Alerts]] - Configure quality-based alerts using these metrics | |||
* [[Charts]] - Visualize metrics over time | |||
* [[Silence_detection]] - Additional audio quality analysis | |||
== AI Summary for RAG == | == AI Summary for RAG == | ||
'''Summary:''' | |||
'''Keywords:''' glossary, packet loss, pdv, jitter, jitter buffer, mos, mos | '''Summary:''' Glossary of VoIP quality metrics and monitoring terms for VoIPmonitor. Covers network metrics (Packet Loss with distribution tracking, PDV/Jitter with threshold intervals, PDD), mitigation mechanisms (Jitter Buffer types, PLC techniques), voice quality measurements (MOS 1-5 scale with codec baselines, VoIPmonitor's parametric MOS calculation using F1/F2/adapt jitter buffer simulations), and carrier metrics (ASR, NER, ACD). Key clarification: VoIPmonitor does NOT calculate R-Factor - use MOS percentiles (%95, %99) and historical trend monitoring instead. RTCP provides endpoint-reported alternative statistics. | ||
'''Keywords:''' glossary, packet loss, pdv, jitter, jitter buffer, mos, mos f1, mos f2, mos adapt, r-factor, pesq, pdd, rtcp, asr, ner, acd, plc, packet loss concealment, percentile, g.711, g.729, codec, quality, kpi, metric, voip quality, parametric mos | |||
'''Key Questions:''' | '''Key Questions:''' | ||
* What is | * What is Packet Delay Variation (PDV) and how does VoIPmonitor measure it? | ||
* How does VoIPmonitor calculate MOS? What are MOS F1, F2, and adapt? | * How does VoIPmonitor calculate MOS? What are MOS F1, F2, and adapt? | ||
* Does VoIPmonitor calculate R-Factor? What should I use instead? | |||
* What is the difference between ASR and NER? | * What is the difference between ASR and NER? | ||
* What is Packet Loss Concealment (PLC)? | * What is Packet Loss Concealment (PLC) and what techniques exist? | ||
* How do I interpret | * How do I interpret MOS percentile scores like %95? | ||
* What is a Jitter Buffer and what | * What is a Jitter Buffer and what types exist? | ||
* What MOS score should I expect for different codecs? | |||
Latest revision as of 16:59, 8 January 2026
Quick reference for VoIP quality metrics and monitoring concepts used in VoIPmonitor.
Network Quality Metrics
Packet Loss
Lost data packets cause audible gaps, clicks, or dropouts. Common causes: congestion, faulty hardware, misconfiguration.
VoIPmonitor approach: Records loss distribution (how many consecutive packets lost in various intervals) rather than just average percentage. This matters because 2% random loss is far less noticeable than a 2-second burst of 100% loss.
Packet Delay Variation (PDV) / Jitter
Variation in packet arrival times from expected intervals. High jitter = erratic packet bursts = degraded quality even without packet loss.
VoIPmonitor approach: Measures packets exceeding delay thresholds:
- 50–70ms, 70–90ms, 90–120ms, 120–150ms, 150–300ms, >300ms
ℹ️ Note: Constant jitter values (same value throughout call) indicate clock mismatch in device, not network issues. Zero jitter with large initial delay = one-time buffering spike, not ongoing jitter.
Post-Dial Delay (PDD)
Time from last digit dialed to first feedback (ringback/busy tone). Long PDD causes users to hang up prematurely.
Mitigation Mechanisms
Jitter Buffer
Temporary storage at receiving end that delays and reorders packets for smooth playback. Types:
- Fixed: Constant buffer size
- Adaptive: Dynamically adjusts based on network conditions
Packet Loss Concealment (PLC)
Masks lost packets since retransmission is not feasible in real-time voice:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Zero Insertion | Replace with silence (crudest method) |
| Waveform Substitution | Repeat last known frame (common, per G.711 Appendix I) |
| Model-Based | Interpolate missing audio using speech models (best quality) |
Voice Quality Metrics
Mean Opinion Score (MOS)
MOS is a standardized numerical rating of perceived voice quality, ranging from 1 (bad) to 5 (excellent). Originally a subjective test where human listeners would rate call quality, it is now typically calculated objectively using algorithms like the one defined in the ITU-T P.862 (PESQ) standard.
| MOS | Quality | Impairment |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Excellent | Imperceptible |
| 4 | Good | Perceptible but not annoying |
| 3 | Fair | Slightly annoying |
| 2 | Poor | Annoying |
| 1 | Bad | Very annoying |
Codec baseline scores:
| Codec | Bitrate | Typical MOS |
|---|---|---|
| G.711 | 64 kbit/s | 4.1 |
| iLBC | 15.2 kbit/s | 4.14 |
| AMR | 12.2 kbit/s | 4.14 |
| G.729 | 8 kbit/s | 3.92 |
| G.723.1 | 6.3 kbit/s | 3.9 |
VoIPmonitor MOS Calculation
VoIPmonitor calculates parametric MOS from network metrics (packet loss, PDV), not the audio signal. It simulates jitter buffer performance:
| Score | Jitter Buffer Model | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| MOS F1 | Fixed 50ms | Very sensitive to jitter |
| MOS F2 | Fixed 200ms | Moderate tolerance |
| MOS adapt | Adaptive up to 500ms | Real-world endpoint simulation |
Default calculation uses G.711 codec with PLC for consistent cross-call comparison.
R-Factor
⚠️ Warning: VoIPmonitor does NOT calculate R-Factor. R-Factor (ITU-T G.107 E-Model, 0-100 scale) is redundant because MOS provides equivalent information with direct mathematical correlation.
Recommended approach instead:
- Track MOS percentiles (%95, %99) not averages
- Monitor changes over time against historical baselines
- Use VoIPmonitor's aggregation by source IP/number
RTCP
RTP Control Protocol provides endpoint-reported statistics: transmitted/lost packets, jitter, round-trip delay. VoIPmonitor parses RTCP reports for alternative view of call quality.
Carrier-Grade Metrics
ASR (Answer-Seizure Ratio)
Percentage of answered calls from total attempts (ITU E.411):
ASR = (Answered Calls / Total Seizures) × 100
Low ASR can indicate network problems but is also affected by user behavior (busy, no answer).
NER (Network Effectiveness Ratio)
Like ASR but measures only network capability—calls reaching destination but rejected by user (busy, no answer) count as "successful." Configure which SIP codes are successful in Settings.
ACD (Average Call Duration)
Average length of answered calls. Low ACD combined with low ASR often indicates quality problems (users hanging up due to poor audio).
Statistical Concepts
Percentiles
Value below which a given percentage of observations falls.
Example: MOS %95 = 3.2 means 5% of calls had MOS of 3.2 or worse. More useful than averages for identifying systemic problems.
See Also
- Comprehensive_Guide_to_VoIP_Voice_Quality - Detailed voice quality analysis
- Alerts - Configure quality-based alerts using these metrics
- Charts - Visualize metrics over time
- Silence_detection - Additional audio quality analysis
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: Glossary of VoIP quality metrics and monitoring terms for VoIPmonitor. Covers network metrics (Packet Loss with distribution tracking, PDV/Jitter with threshold intervals, PDD), mitigation mechanisms (Jitter Buffer types, PLC techniques), voice quality measurements (MOS 1-5 scale with codec baselines, VoIPmonitor's parametric MOS calculation using F1/F2/adapt jitter buffer simulations), and carrier metrics (ASR, NER, ACD). Key clarification: VoIPmonitor does NOT calculate R-Factor - use MOS percentiles (%95, %99) and historical trend monitoring instead. RTCP provides endpoint-reported alternative statistics.
Keywords: glossary, packet loss, pdv, jitter, jitter buffer, mos, mos f1, mos f2, mos adapt, r-factor, pesq, pdd, rtcp, asr, ner, acd, plc, packet loss concealment, percentile, g.711, g.729, codec, quality, kpi, metric, voip quality, parametric mos
Key Questions:
- What is Packet Delay Variation (PDV) and how does VoIPmonitor measure it?
- How does VoIPmonitor calculate MOS? What are MOS F1, F2, and adapt?
- Does VoIPmonitor calculate R-Factor? What should I use instead?
- What is the difference between ASR and NER?
- What is Packet Loss Concealment (PLC) and what techniques exist?
- How do I interpret MOS percentile scores like %95?
- What is a Jitter Buffer and what types exist?
- What MOS score should I expect for different codecs?