Silence detection: Difference between revisions
(Add section explaining how to use silence detection for identifying calls with background noise and differentiating between caller/called party noise) |
(Rewrite: consolidated structure, added parameter table, See Also section, improved formatting) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Category:GUI manual]] | [[Category:GUI manual]] | ||
'''This guide explains | '''This guide explains VoIPmonitor's audio analysis features for G.711 codecs, including silence and clipping detection. These tools diagnose audio quality issues not caused by network problems, such as one-way audio, muted microphones, or faulty hardware.''' | ||
== Overview | == Overview == | ||
Standard network metrics | |||
Standard network metrics (packet loss, jitter) only identify transport-layer problems. Many audio issues originate at endpoints. The Silence & Clipping Detection engine analyzes decoded G.711 audio to identify these problems. | |||
<kroki lang="plantuml"> | <kroki lang="plantuml"> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
</kroki> | </kroki> | ||
'''Use cases:''' | |||
* | * "Dead air" complaints when network statistics look perfect | ||
* One-way audio | * One-way audio (one party not transmitting) | ||
* | * Audio clipping (clicks or distortion) | ||
* | * Accurate [[Glossary|MOS]] calculation by penalizing silence periods | ||
* | * Detecting calls in noisy environments (see [[#Detecting Calls with Background Noise|below]]) | ||
== Prerequisites == | == Prerequisites == | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Requirement !! Details | |||
|- | |||
| '''Codec''' || G.711 a-law/u-law only. Other codecs are not analyzed. | |||
|- | |||
| '''CPU''' || Audio decoding is CPU-intensive. Monitor system load after enabling. | |||
|- | |||
| '''Database''' || Modern installations (2020+) have required columns. Legacy systems may need schema updates (see below). | |||
|} | |||
== Configuration == | |||
=== Parameters === | |||
== | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |||
! Parameter !! Default !! Description | |||
|- | |||
| <code>silencedetect</code> || no || Enable silence detection and MOS adjustment | |||
|- | |||
| <code>clippingdetect</code> || no || Enable audio clipping detection | |||
|- | |||
| <code>silencethreshold</code> || 512 || Audio level threshold for silence. Lower = stricter detection. | |||
|} | |||
=== | === Enable in voipmonitor.conf === | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="ini"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="ini"> | ||
# | # /etc/voipmonitor.conf | ||
silencedetect = yes | silencedetect = yes | ||
clippingdetect = yes | clippingdetect = yes | ||
silencethreshold = 512 | silencethreshold = 512 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 78: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
= | {{Note|1=For legacy installations (pre-2020) that report missing columns on startup, add them via SQL: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sql"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="sql"> | ||
ALTER TABLE cdr | ALTER TABLE cdr | ||
| Line 89: | Line 92: | ||
ADD COLUMN b_mos_silence_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL; | ADD COLUMN b_mos_silence_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL; | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
}} | |||
== Features & Metrics == | == Features & Metrics == | ||
=== | === Silence as Packet Loss (MOS Adjustment) === | ||
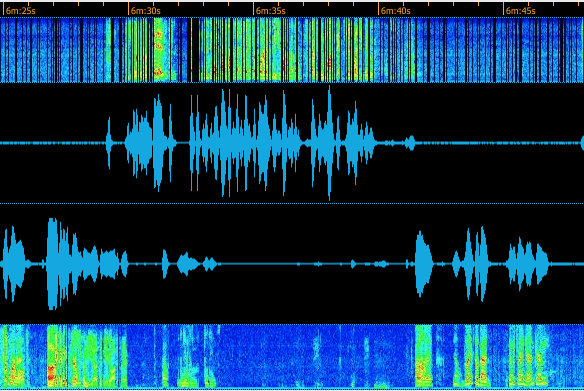
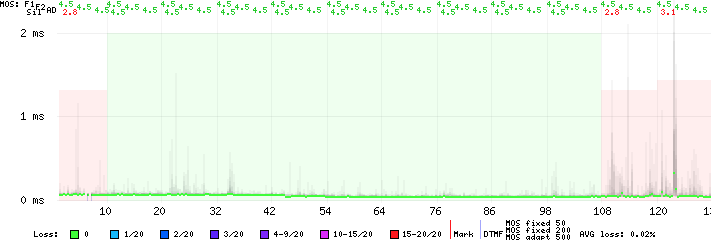
Silence frames (e.g., muted mic) are treated as packet loss, allowing accurate [[Glossary|MOS]] calculation for silent calls. In CDR Graph Detail, a new '''"Sil"''' (Silence MOS) score appears. | |||
[[File:cdr_spectral_silence_example.png]] | [[File:cdr_spectral_silence_example.png]] | ||
[[File:cdr_graph_silence_lowmos_example.png]] | |||
=== Overall Silence Percentage === | |||
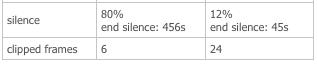
CDR Detail shows total silence percentage for caller and callee streams. | |||
= | {{Tip|1=>95% silence in one direction strongly indicates one-way audio.}} | ||
[[File:cdr_detail_silence_table.png]] | [[File:cdr_detail_silence_table.png]] | ||
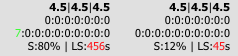
=== | === Silence at End of Call === | ||
Measures silence duration before hangup. High values may indicate user frustration (couldn't hear other party). Shown in main CDR listing. | |||
[[File:cdr_summary_silence_example.png]] | [[File:cdr_summary_silence_example.png]] | ||
=== | === Audio Clipping Detection === | ||
Counts clipped frames (signal too loud, hits max amplitude = distortion). Shown in CDR detail; usable for filtering and charts to find problematic endpoints. | |||
[[File:charts_silence_values.png]] | [[File:charts_silence_values.png]] | ||
=== | === MOS During Silence Periods === | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 124: | Line 129: | ||
! Column !! Description | ! Column !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <code>a_mos_silence_mult10</code> / <code>b_mos_silence_mult10</code> || | | <code>a_mos_silence_mult10</code> / <code>b_mos_silence_mult10</code> || Average MOS during silence (caller/callee) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <code>a_mos_silence_min_mult10</code> / <code>b_mos_silence_min_mult10</code> || | | <code>a_mos_silence_min_mult10</code> / <code>b_mos_silence_min_mult10</code> || Minimum MOS during silence (caller/callee) | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{Note|These metrics only populate when <code>silencedetect=yes</code>. Otherwise, regular MOS is shown.}} | |||
== Detecting Calls with Background Noise == | |||
''' | Calls with background noise show '''low silence percentage''' because continuous audio prevents silence detection. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! Environment !! Silence % Range | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Clean / quiet office | | | Clean/quiet office || 40-70% | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Environmental noise ( | | Environmental noise (A/C, distant voices) || 10-39% | ||
|- | |- | ||
| High noise (factory | | High noise (factory, crowded call center) || 0-9% | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Workflow | '''Workflow:''' | ||
# Enable <code>silencedetect=yes</code> with appropriate <code>silencethreshold</code> | |||
# Filter CDR for <code>Caller Silence < 20%</code> OR <code>Called Silence < 20%</code> | |||
# Review flagged calls' audio recordings to confirm noise | |||
# Create saved filters or [[Alerts|alerts]] for ongoing monitoring | |||
{{Tip|Use spectral analysis in CDR Graph Detail to distinguish white/brown noise (continuous spectrum) from sporadic noise (intermittent) and genuine speech (natural patterns with pauses).}} | |||
== See Also == | |||
* [[Glossary]] - MOS, jitter, packet loss definitions | |||
* [[Comprehensive_Guide_to_VoIP_Voice_Quality]] - Voice quality factors | |||
* [[Call_Detail_Record_-_CDR]] - CDR view and filtering | |||
* [[Charts]] - Creating charts from silence/clipping data | |||
* [[Alerts]] - Setting up alerts for quality thresholds | |||
== AI Summary for RAG == | |||
'''Summary:''' VoIPmonitor's Silence and Clipping Detection analyzes G.711 (a-law/u-law) audio to diagnose issues invisible to network metrics. Key features: treats silence as packet loss for accurate MOS calculation, calculates silence percentage (>95% indicates one-way audio), measures end-of-call silence (user frustration indicator), counts clipped frames (distortion), and detects calls with background noise (low silence %). Configuration requires <code>silencedetect=yes</code> and <code>clippingdetect=yes</code> in voipmonitor.conf. Modern installations have required database columns by default. | |||
'''Summary:''' VoIPmonitor's Silence and Clipping Detection analyzes G.711 (a-law/u-law) audio to diagnose issues invisible to network metrics. Key features: treats silence as packet loss for accurate MOS, calculates silence percentage (>95% indicates one-way audio), measures end-of-call silence, counts clipped frames, and | |||
'''Keywords:''' silence detection, clipping, one-way audio, dead air, MOS, G.711, silencedetect, clippingdetect, silencethreshold, mos_silence, background noise, noisy environments | '''Keywords:''' silence detection, clipping, one-way audio, dead air, MOS, G.711, silencedetect, clippingdetect, silencethreshold, mos_silence, background noise, noisy environments, audio analysis, endpoint issues | ||
'''Key Questions:''' | '''Key Questions:''' | ||
| Line 181: | Line 177: | ||
* Why is a call's MOS score high even though the user reported hearing nothing? | * Why is a call's MOS score high even though the user reported hearing nothing? | ||
* How does VoIPmonitor detect silence in a call? | * How does VoIPmonitor detect silence in a call? | ||
* What does the "Silence MOS | * What does the "Sil" (Silence MOS) score mean in the CDR graph? | ||
* How can I find calls with audio clipping? | * How can I find calls with audio clipping? | ||
* How can I filter calls based on background noise | * How can I filter calls based on background noise? | ||
* What silence percentage indicates a noisy environment? | |||
Latest revision as of 16:47, 8 January 2026
This guide explains VoIPmonitor's audio analysis features for G.711 codecs, including silence and clipping detection. These tools diagnose audio quality issues not caused by network problems, such as one-way audio, muted microphones, or faulty hardware.
Overview
Standard network metrics (packet loss, jitter) only identify transport-layer problems. Many audio issues originate at endpoints. The Silence & Clipping Detection engine analyzes decoded G.711 audio to identify these problems.
Use cases:
- "Dead air" complaints when network statistics look perfect
- One-way audio (one party not transmitting)
- Audio clipping (clicks or distortion)
- Accurate MOS calculation by penalizing silence periods
- Detecting calls in noisy environments (see below)
Prerequisites
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Codec | G.711 a-law/u-law only. Other codecs are not analyzed. |
| CPU | Audio decoding is CPU-intensive. Monitor system load after enabling. |
| Database | Modern installations (2020+) have required columns. Legacy systems may need schema updates (see below). |
Configuration
Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
silencedetect |
no | Enable silence detection and MOS adjustment |
clippingdetect |
no | Enable audio clipping detection |
silencethreshold |
512 | Audio level threshold for silence. Lower = stricter detection. |
Enable in voipmonitor.conf
# /etc/voipmonitor.conf
silencedetect = yes
clippingdetect = yes
silencethreshold = 512
systemctl restart voipmonitor
ℹ️ Note: For legacy installations (pre-2020) that report missing columns on startup, add them via SQL:
ALTER TABLE cdr
ADD COLUMN caller_silence tinyint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN called_silence tinyint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN caller_silence_end smallint default NULL,
ADD COLUMN called_silence_end smallint default NULL,
ADD COLUMN caller_clipping_div3 smallint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN called_clipping_div3 smallint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN a_mos_silence_min_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
ADD COLUMN b_mos_silence_min_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
ADD COLUMN a_mos_silence_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
ADD COLUMN b_mos_silence_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL;
Features & Metrics
Silence as Packet Loss (MOS Adjustment)
Silence frames (e.g., muted mic) are treated as packet loss, allowing accurate MOS calculation for silent calls. In CDR Graph Detail, a new "Sil" (Silence MOS) score appears.
Overall Silence Percentage
CDR Detail shows total silence percentage for caller and callee streams.
💡 Tip: >95% silence in one direction strongly indicates one-way audio.
Silence at End of Call
Measures silence duration before hangup. High values may indicate user frustration (couldn't hear other party). Shown in main CDR listing.
Audio Clipping Detection
Counts clipped frames (signal too loud, hits max amplitude = distortion). Shown in CDR detail; usable for filtering and charts to find problematic endpoints.
MOS During Silence Periods
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
a_mos_silence_mult10 / b_mos_silence_mult10 |
Average MOS during silence (caller/callee) |
a_mos_silence_min_mult10 / b_mos_silence_min_mult10 |
Minimum MOS during silence (caller/callee) |
ℹ️ Note:
Detecting Calls with Background Noise
Calls with background noise show low silence percentage because continuous audio prevents silence detection.
| Environment | Silence % Range |
|---|---|
| Clean/quiet office | 40-70% |
| Environmental noise (A/C, distant voices) | 10-39% |
| High noise (factory, crowded call center) | 0-9% |
Workflow:
- Enable
silencedetect=yeswith appropriatesilencethreshold - Filter CDR for
Caller Silence < 20%ORCalled Silence < 20% - Review flagged calls' audio recordings to confirm noise
- Create saved filters or alerts for ongoing monitoring
💡 Tip: Use spectral analysis in CDR Graph Detail to distinguish white/brown noise (continuous spectrum) from sporadic noise (intermittent) and genuine speech (natural patterns with pauses).
See Also
- Glossary - MOS, jitter, packet loss definitions
- Comprehensive_Guide_to_VoIP_Voice_Quality - Voice quality factors
- Call_Detail_Record_-_CDR - CDR view and filtering
- Charts - Creating charts from silence/clipping data
- Alerts - Setting up alerts for quality thresholds
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: VoIPmonitor's Silence and Clipping Detection analyzes G.711 (a-law/u-law) audio to diagnose issues invisible to network metrics. Key features: treats silence as packet loss for accurate MOS calculation, calculates silence percentage (>95% indicates one-way audio), measures end-of-call silence (user frustration indicator), counts clipped frames (distortion), and detects calls with background noise (low silence %). Configuration requires silencedetect=yes and clippingdetect=yes in voipmonitor.conf. Modern installations have required database columns by default.
Keywords: silence detection, clipping, one-way audio, dead air, MOS, G.711, silencedetect, clippingdetect, silencethreshold, mos_silence, background noise, noisy environments, audio analysis, endpoint issues
Key Questions:
- How can I diagnose one-way audio problems?
- Why is a call's MOS score high even though the user reported hearing nothing?
- How does VoIPmonitor detect silence in a call?
- What does the "Sil" (Silence MOS) score mean in the CDR graph?
- How can I find calls with audio clipping?
- How can I filter calls based on background noise?
- What silence percentage indicates a noisy environment?