Capture rules: Difference between revisions
(Fix image display - use thumb|none to prevent floating into Troubleshooting section) |
(Merge Capture_rules_-_reload content, add database manipulation section, improve diagrams and formatting) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
skinparam shadowing false | skinparam shadowing false | ||
skinparam defaultFontName Arial | skinparam defaultFontName Arial | ||
skinparam rectangle { | |||
BorderColor #4A90E2 | |||
BackgroundColor #FFFFFF | |||
} | |||
rectangle "GUI" as gui | rectangle "GUI\n(Web Interface)" as gui | ||
rectangle "Sensor\n(Manager API\nport 5029)" as sensor | rectangle "Sensor\n(Manager API\nport 5029)" as sensor | ||
database "voipmonitor.conf | database "MySQL\nfilter_ip\nfilter_telnum" as db | ||
file "voipmonitor.conf" as config | |||
gui -> sensor : reload | gui -down-> db : 1. Save rules | ||
sensor -> config : | gui -right-> sensor : 2. Send reload | ||
sensor -> gui : | sensor -down-> db : 3. Re-read rules | ||
sensor -left-> config : 3. Re-read config | |||
sensor -up-> gui : 4. Success/error | |||
note bottom of sensor | |||
Rules take effect only | |||
after reload command | |||
end note | |||
@enduml | @enduml | ||
</kroki> | </kroki> | ||
| Line 48: | Line 60: | ||
! Option !! Description | ! Option !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Skip''' || Ignores matched calls entirely - no files are created, no RTP analysis is performed, and no CDR is generated | | '''Skip''' || Ignores matched calls entirely - no files are created, no RTP analysis is performed, and no CDR is generated. Use this to completely exclude certain traffic from monitoring. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Auto remove at''' || Automatically deletes the rule on a specified date | | '''Auto remove at''' || Automatically deletes the rule on a specified date. Useful for temporary debugging rules that should not persist indefinitely. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 66: | Line 78: | ||
# Click the green '''reload sniffer''' button to apply changes | # Click the green '''reload sniffer''' button to apply changes | ||
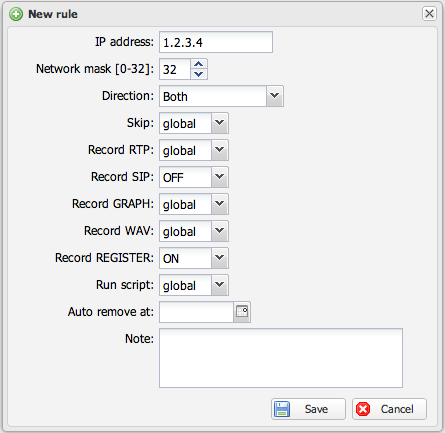
[[File:capturerules-ip.png|thumb|none| | [[File:capturerules-ip.png|thumb|none|500px|IP-based capture rule configuration]] | ||
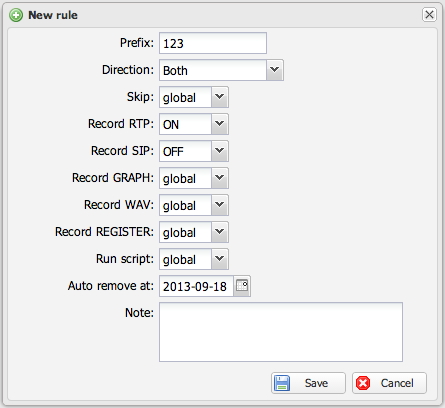
[[File:capturerules-tel.png|thumb|none| | [[File:capturerules-tel.png|thumb|none|500px|Telephone number-based capture rule configuration]] | ||
<br clear="all"/> | <br clear="all"/> | ||
== | == Advanced: Managing Rules via Database == | ||
For automation, bulk operations, or scripted deployments, you can manipulate capture rules directly in the MySQL database. This method is ideal for: | |||
* Automated provisioning systems | |||
* Bulk rule creation | |||
* Integration with external management tools | |||
* Remote sensor management without GUI access | |||
=== Database Tables === | |||
Capture rules are stored in two tables in the <code>voipmonitor</code> database: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Table !! Purpose | |||
|- | |||
| <code>filter_ip</code> || IP address and subnet-based rules | |||
|- | |||
| <code>filter_telnum</code> || Telephone number prefix-based rules | |||
|} | |||
=== Adding IP-Based Rules === | |||
Rules in the <code>filter_ip</code> table match source or destination IP addresses or subnets. | |||
'''Key Columns:''' | |||
=== | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |||
! Column !! Type !! Description | |||
|- | |||
| <code>ip</code> || INT UNSIGNED || IP address converted using <code>INET_ATON()</code> | |||
|- | |||
| <code>mask</code> || TINYINT || Subnet mask in CIDR notation (e.g., <code>24</code> for /24) | |||
|- | |||
| <code>direction</code> || TINYINT || <code>0</code> = both, <code>1</code> = source, <code>2</code> = destination | |||
|- | |||
| <code>rtp</code> || TINYINT || <code>1</code> = SAVE, <code>2</code> = DISCARD, <code>3</code> = header only | |||
|} | |||
'''Example:''' Force-save RTP for all calls from or to the <code>1.2.3.0/24</code> network: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sql"> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=" | INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_ip | ||
(ip, mask, direction, rtp) | |||
VALUES | |||
(INET_ATON('1.2.3.0'), 24, 0, 1); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== Adding Telephone Number-Based Rules === | |||
Rules in the <code>filter_telnum</code> table match caller or called number prefixes. | |||
'''Key Columns:''' | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! Column !! Type !! Description | ||
|- | |||
| <code>prefix</code> || VARCHAR || Telephone number prefix to match (e.g., <code>4420</code>) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <code>fixed_len</code> || TINYINT || Fixed length matching (0 = prefix match) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <code>direction</code> || TINYINT || <code>0</code> = both, <code>1</code> = caller, <code>2</code> = called | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | <code>rtp</code> || TINYINT || <code>1</code> = SAVE, <code>2</code> = DISCARD, <code>3</code> = header only | ||
|} | |} | ||
= | '''Example 1:''' Match any direction - force RTP saving when caller or called number starts with <code>12345</code>: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sql"> | |||
INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_telnum | |||
(prefix, fixed_len, direction, rtp) | |||
VALUES | |||
('12345', 0, 0, 1); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
'''Example 2:''' Match only destination - force RTP saving only when the '''called''' number starts with <code>98765</code>: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="sql"> | |||
INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_telnum | |||
(prefix, fixed_len, direction, rtp) | |||
VALUES | |||
('98765', 0, 2, 1); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== | == Reloading Rules == | ||
After adding or modifying rules (via GUI or database), you must signal the sniffer to reload them. Rules '''do not''' take effect until reloaded. | |||
=== Method 1: GUI Reload Button (Recommended) === | |||
# Log in to the VoIPmonitor GUI | # Log in to the VoIPmonitor GUI | ||
| Line 114: | Line 182: | ||
# Check for error messages if reload fails | # Check for error messages if reload fails | ||
=== Method 2: Manager API (CLI) === | |||
For directly accessible sensors, send a reload command to the Manager API port (default 5029): | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
echo 'reload' | nc | # Replace SENSOR_IP with your sensor's IP address | ||
echo 'reload' | nc SENSOR_IP 5029 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Use this method | Use this method for automation or when GUI access is not available. | ||
=== Method 3: Server API (Client/Server Mode) === | |||
If sensors are in [[Sniffer_distributed_architecture|client/server mode]] and Manager API ports are not directly accessible, send commands via the central server. | |||
= | <kroki lang="plantuml"> | ||
@startuml | |||
skinparam shadowing false | |||
skinparam defaultFontName Arial | |||
actor Admin | |||
rectangle "Central Server" as server { | |||
rectangle "Manager API\nport 5029" as mgr | |||
rectangle "Server API\nport 60024" as sapi | |||
} | |||
rectangle "Remote Sensor\n(behind NAT)" as sensor | |||
Admin -> mgr : 1. list_active_clients | |||
mgr -> Admin : sensor_id list | |||
Admin -> sapi : 2. reload command\n(with sensor_id) | |||
sapi -> sensor : 3. forward reload | |||
@enduml | |||
</kroki> | |||
'''Step 1:''' Get list of connected sensors and their IDs: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
echo 'list_active_clients' | nc SERVER_IP 5029 | echo 'list_active_clients' | nc SERVER_IP 5029 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Example output: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="json"> | |||
{"count":1,"services":[{"ip":"127.0.0.1","port":54137,"sensor_id":114}]} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
'''Step 2:''' Send reload command via Server API port (default 60024): | |||
echo '{"type_connection":"gui_command","sensor_id": | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
echo '{"type_connection":"gui_command","sensor_id":114,"command":"reload"}' | nc SERVER_IP 60024 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
The central server forwards the command to the specified remote sensor over its secure channel. | |||
== Troubleshooting == | |||
If changes made to capture rules in the GUI are not being applied, the most common cause is that the reload signal did not reach the sensor due to network connectivity issues. | |||
=== Step 1: Test Manager API Connectivity === | |||
Before attempting a reload, verify that the GUI can reach the sensor's Manager API port. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
# Replace SENSOR_IP with your sensor's actual IP address | |||
echo 'getversion' | nc SENSOR_IP 5029 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Result !! Meaning !! Action | |||
|- | |||
| Version string (e.g., <code>voipmonitor 8.0.0-SVN.10</code>) || Connectivity OK || Proceed to reload | |||
|- | |||
| No output / connection times out || Network problem || Check firewall and routing | |||
|- | |||
| Connection refused || Manager API not running || Check sensor service status | |||
|} | |||
==== Common Connectivity Issues ==== | |||
=== Step | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |||
! Issue !! Solution | |||
|- | |||
| Firewall blocking port 5029 || Ensure port 5029/TCP is open on the sensor's firewall | |||
|- | |||
| Wrong IP in Settings > Sensors || Verify the Manager IP matches the sensor's actual IP address | |||
|- | |||
| NAT/Routing issues || For sensors behind NAT, use the Server API method (Method 3 above) | |||
|} | |||
=== Step 2: Immediate Workaround - Restart Sniffer === | |||
If | If reload fails and connectivity cannot be resolved immediately, restart the sniffer service: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| Line 147: | Line 283: | ||
systemctl status voipmonitor | systemctl status voipmonitor | ||
# Restart | # Restart (forces full reload of all rules) | ||
systemctl restart voipmonitor | systemctl restart voipmonitor | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Note: Restarting causes a brief interruption in call monitoring. | |||
=== Verifying Rules Are Active === | === Verifying Rules Are Active === | ||
After reloading rules, verify they are | After reloading rules, verify they are applied: | ||
'''1. Check logs for reload confirmation:''' | '''1. Check logs for reload confirmation:''' | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
# Debian/Ubuntu | # Debian/Ubuntu | ||
| Line 172: | Line 311: | ||
=== Preventing Future Issues === | === Preventing Future Issues === | ||
* Ensure '''stable network connectivity''' between GUI and sensors | * Ensure '''stable network connectivity''' between GUI and sensors | ||
* '''Use monitoring tools''' to detect | * '''Use monitoring tools''' to detect connectivity issues early | ||
* Consider '''client/server mode''' | * Consider '''client/server mode''' for sensors in different networks - uses persistent connections that are more reliable than direct Manager API access | ||
== AI Summary for RAG == | == AI Summary for RAG == | ||
'''Summary:''' This article explains VoIPmonitor's capture rules for selective call recording based on IP addresses or phone numbers. It covers rule configuration options (3-state GLOBAL/ON/OFF, Skip, Auto remove), GUI usage, and script integration via filtercommand. The | '''Summary:''' This article explains VoIPmonitor's capture rules for selective call recording based on IP addresses or phone numbers. It covers rule configuration options (3-state GLOBAL/ON/OFF, Skip for ignoring calls, Auto remove for temporary rules), GUI usage, and script integration via filtercommand. The advanced section explains how to programmatically manage rules by directly inserting into the <code>filter_ip</code> and <code>filter_telnum</code> MySQL tables, with detailed column explanations and SQL examples using <code>INET_ATON()</code> for IP conversion. Three reload methods are documented: GUI button (recommended), CLI via Manager API (<code>echo 'reload' | nc</code>), and Server API for client/server deployments using <code>list_active_clients</code> and JSON commands. The troubleshooting section explains how to diagnose connectivity issues using the <code>getversion</code> command, common problems (firewall, wrong IP, NAT), and verification steps. | ||
'''Keywords:''' capture rules, selective recording, RTP packets, SIP signaling, sniffer reload, GLOBAL option, skip calls, auto-remove, filtercommand, manager api, getversion, port 5029, troubleshooting, | '''Keywords:''' capture rules, selective recording, RTP packets, SIP signaling, filter_ip, filter_telnum, INET_ATON, database, SQL, sniffer reload, GLOBAL option, skip calls, auto-remove, filtercommand, manager api, server api, getversion, port 5029, port 60024, list_active_clients, troubleshooting, client server mode | ||
'''Key Questions:''' | '''Key Questions:''' | ||
| Line 189: | Line 328: | ||
* How can I auto-delete a rule after a certain date? | * How can I auto-delete a rule after a certain date? | ||
* Can rules trigger external scripts? | * Can rules trigger external scripts? | ||
* How can I add capture rules without using the GUI? | |||
* How to add IP or telephone number based filters directly to the database? | |||
* What do the direction and rtp columns mean in the filter_ip table? | |||
* Why are capture rules not being applied after I change them in the GUI? | * Why are capture rules not being applied after I change them in the GUI? | ||
* How do I test if the GUI can reach the sensor's Manager API? | * How do I test if the GUI can reach the sensor's Manager API? | ||
* How can I reload capture rules if the sensor is behind NAT? | * How can I reload capture rules if the sensor is behind NAT? | ||
* How do I reload rules on a remote sensor in client/server mode? | |||
* How do I verify that capture rules have been reloaded? | * How do I verify that capture rules have been reloaded? | ||
[[Category:GUI manual]] | [[Category:GUI manual]] | ||
[[Category:Sniffer Configuration]] | [[Category:Sniffer Configuration]] | ||
Revision as of 22:55, 4 January 2026
Capture rules allow selective recording of calls to disk based on IP addresses or phone numbers. By default, RTP packets may not be fully saved (or only headers are stored), but rules can enable full RTP recording, call graphs, or SIP signaling capture for specific calls. Rules can also trigger external shell scripts for custom processing.
How Capture Rules Work
The sniffer loads capture rules on startup and supports hot-reloading without service restart. Changes made in the GUI are not automatically applied to the running sniffer - you must click the green "reload sniffer" button in the control panel to apply them.
Rule Options
Capture rules support the following configuration options:
3-State Options
Some options use a 3-state selector:
| State | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| GLOBAL | Inherits from global sniffer configuration | Enable SIP REGISTER for specific IPs without overriding RTP settings |
| ON | Explicitly enables the option | Force RTP recording for matched calls |
| OFF | Explicitly disables the option | Disable recording for matched calls |
Special Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Skip | Ignores matched calls entirely - no files are created, no RTP analysis is performed, and no CDR is generated. Use this to completely exclude certain traffic from monitoring. |
| Auto remove at | Automatically deletes the rule on a specified date. Useful for temporary debugging rules that should not persist indefinitely. |
Script Integration
Rules can trigger external shell scripts when calls match. Configure this via the filtercommand option in voipmonitor.conf. See Sniffer_configuration#filtercommand for details.
GUI Usage
Access capture rules via the GUI control panel:
- Navigate to Control Panel (Dashboard)
- Click on Capture Rules section
- Create rules using IP or TEL number filters
- Click the green reload sniffer button to apply changes
Advanced: Managing Rules via Database
For automation, bulk operations, or scripted deployments, you can manipulate capture rules directly in the MySQL database. This method is ideal for:
- Automated provisioning systems
- Bulk rule creation
- Integration with external management tools
- Remote sensor management without GUI access
Database Tables
Capture rules are stored in two tables in the voipmonitor database:
| Table | Purpose |
|---|---|
filter_ip |
IP address and subnet-based rules |
filter_telnum |
Telephone number prefix-based rules |
Adding IP-Based Rules
Rules in the filter_ip table match source or destination IP addresses or subnets.
Key Columns:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ip |
INT UNSIGNED | IP address converted using INET_ATON()
|
mask |
TINYINT | Subnet mask in CIDR notation (e.g., 24 for /24)
|
direction |
TINYINT | 0 = both, 1 = source, 2 = destination
|
rtp |
TINYINT | 1 = SAVE, 2 = DISCARD, 3 = header only
|
Example: Force-save RTP for all calls from or to the 1.2.3.0/24 network:
INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_ip
(ip, mask, direction, rtp)
VALUES
(INET_ATON('1.2.3.0'), 24, 0, 1);
Adding Telephone Number-Based Rules
Rules in the filter_telnum table match caller or called number prefixes.
Key Columns:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
prefix |
VARCHAR | Telephone number prefix to match (e.g., 4420)
|
fixed_len |
TINYINT | Fixed length matching (0 = prefix match) |
direction |
TINYINT | 0 = both, 1 = caller, 2 = called
|
rtp |
TINYINT | 1 = SAVE, 2 = DISCARD, 3 = header only
|
Example 1: Match any direction - force RTP saving when caller or called number starts with 12345:
INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_telnum
(prefix, fixed_len, direction, rtp)
VALUES
('12345', 0, 0, 1);
Example 2: Match only destination - force RTP saving only when the called number starts with 98765:
INSERT INTO voipmonitor.filter_telnum
(prefix, fixed_len, direction, rtp)
VALUES
('98765', 0, 2, 1);
Reloading Rules
After adding or modifying rules (via GUI or database), you must signal the sniffer to reload them. Rules do not take effect until reloaded.
Method 1: GUI Reload Button (Recommended)
- Log in to the VoIPmonitor GUI
- Navigate to Control Panel (Dashboard)
- Click the green reload sniffer button
- Check for error messages if reload fails
Method 2: Manager API (CLI)
For directly accessible sensors, send a reload command to the Manager API port (default 5029):
# Replace SENSOR_IP with your sensor's IP address
echo 'reload' | nc SENSOR_IP 5029
Use this method for automation or when GUI access is not available.
Method 3: Server API (Client/Server Mode)
If sensors are in client/server mode and Manager API ports are not directly accessible, send commands via the central server.
Step 1: Get list of connected sensors and their IDs:
echo 'list_active_clients' | nc SERVER_IP 5029
Example output:
{"count":1,"services":[{"ip":"127.0.0.1","port":54137,"sensor_id":114}]}
Step 2: Send reload command via Server API port (default 60024):
echo '{"type_connection":"gui_command","sensor_id":114,"command":"reload"}' | nc SERVER_IP 60024
The central server forwards the command to the specified remote sensor over its secure channel.
Troubleshooting
If changes made to capture rules in the GUI are not being applied, the most common cause is that the reload signal did not reach the sensor due to network connectivity issues.
Step 1: Test Manager API Connectivity
Before attempting a reload, verify that the GUI can reach the sensor's Manager API port.
# Replace SENSOR_IP with your sensor's actual IP address
echo 'getversion' | nc SENSOR_IP 5029
| Result | Meaning | Action |
|---|---|---|
Version string (e.g., voipmonitor 8.0.0-SVN.10) |
Connectivity OK | Proceed to reload |
| No output / connection times out | Network problem | Check firewall and routing |
| Connection refused | Manager API not running | Check sensor service status |
Common Connectivity Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Firewall blocking port 5029 | Ensure port 5029/TCP is open on the sensor's firewall |
| Wrong IP in Settings > Sensors | Verify the Manager IP matches the sensor's actual IP address |
| NAT/Routing issues | For sensors behind NAT, use the Server API method (Method 3 above) |
Step 2: Immediate Workaround - Restart Sniffer
If reload fails and connectivity cannot be resolved immediately, restart the sniffer service:
# SSH to the sensor
ssh root@SENSOR_IP
# Check current status
systemctl status voipmonitor
# Restart (forces full reload of all rules)
systemctl restart voipmonitor
Note: Restarting causes a brief interruption in call monitoring.
Verifying Rules Are Active
After reloading rules, verify they are applied:
1. Check logs for reload confirmation:
# Debian/Ubuntu
tail -f /var/log/syslog | grep voipmonitor
# CentOS/RHEL/AlmaLinux
tail -f /var/log/messages | grep voipmonitor
Look for messages like Rules reloaded or capture rules re-read.
2. Make a test call that should trigger your new rule and verify the recording behavior matches expectations.
3. Monitor CDR view to confirm captured/skipped calls match your rule configuration.
Preventing Future Issues
- Ensure stable network connectivity between GUI and sensors
- Use monitoring tools to detect connectivity issues early
- Consider client/server mode for sensors in different networks - uses persistent connections that are more reliable than direct Manager API access
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: This article explains VoIPmonitor's capture rules for selective call recording based on IP addresses or phone numbers. It covers rule configuration options (3-state GLOBAL/ON/OFF, Skip for ignoring calls, Auto remove for temporary rules), GUI usage, and script integration via filtercommand. The advanced section explains how to programmatically manage rules by directly inserting into the filter_ip and filter_telnum MySQL tables, with detailed column explanations and SQL examples using INET_ATON() for IP conversion. Three reload methods are documented: GUI button (recommended), CLI via Manager API (echo 'reload' | nc), and Server API for client/server deployments using list_active_clients and JSON commands. The troubleshooting section explains how to diagnose connectivity issues using the getversion command, common problems (firewall, wrong IP, NAT), and verification steps.
Keywords: capture rules, selective recording, RTP packets, SIP signaling, filter_ip, filter_telnum, INET_ATON, database, SQL, sniffer reload, GLOBAL option, skip calls, auto-remove, filtercommand, manager api, server api, getversion, port 5029, port 60024, list_active_clients, troubleshooting, client server mode
Key Questions:
- How do capture rules work in VoIPmonitor?
- What are the 3-state options (GLOBAL/ON/OFF) for rules?
- How do I reload rules without restarting the sniffer?
- What does the Skip option do?
- How can I auto-delete a rule after a certain date?
- Can rules trigger external scripts?
- How can I add capture rules without using the GUI?
- How to add IP or telephone number based filters directly to the database?
- What do the direction and rtp columns mean in the filter_ip table?
- Why are capture rules not being applied after I change them in the GUI?
- How do I test if the GUI can reach the sensor's Manager API?
- How can I reload capture rules if the sensor is behind NAT?
- How do I reload rules on a remote sensor in client/server mode?
- How do I verify that capture rules have been reloaded?