Groups: Difference between revisions
(Add GUI refresh requirement after creating new groups) |
(Review: opravy formátování (nezavřené nadpisy), odstranění duplicitní sekce, přesun GUI refresh sekce, změna <pre> na <syntaxhighlight>, přidání mermaid diagramu, regex tabulka) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[[File:groups.png|center|600px|Groups management interface]] | [[File:groups.png|center|600px|Groups management interface]] | ||
=== Important: GUI Refresh Required === | |||
After creating a new group (IP, telephone number, or email), the group may not immediately appear in dropdown lists used throughout the GUI (such as CDR filter templates, alert configurations, or charts). This is because the GUI loads available groups at login time. | |||
'''Solution:''' | |||
# Log out of the GUI | |||
# Log back in | |||
# The newly created group will now appear in all relevant dropdowns | |||
This applies to all group types when used in: | |||
* CDR filter templates (Caller Groups, Called Groups dropdowns) | |||
* Alert configurations | |||
* Charts filters | |||
* Any other GUI component that uses groups | |||
== IP Groups == | == IP Groups == | ||
| Line 33: | Line 48: | ||
# Configure the '''Trunk''', '''Server''', or '''SIP history group''' checkboxes as applicable (see below) | # Configure the '''Trunk''', '''Server''', or '''SIP history group''' checkboxes as applicable (see below) | ||
# Save the group | # Save the group | ||
=== Example IP Group Entries === | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | |||
192.168.1.100 | |||
10.0.0.0/24 | |||
172.16.0.0/16 | |||
2001:db8::1/128 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== Trunk Checkbox === | === Trunk Checkbox === | ||
The '''Trunk''' checkbox | The '''Trunk''' checkbox marks the IPs in this group as belonging to an external SIP trunk (e.g., your VoIP provider or carrier). | ||
=== Server Checkbox === | === Server Checkbox === | ||
| Line 45: | Line 69: | ||
The '''SIP history group''' checkbox merges private and public IP addresses into a single column in the SIP ladder/history view. This is particularly useful for devices behind NAT (Network Address Translation) where the SIP signaling shows public IP addresses while RTP media uses private IP addresses. | The '''SIP history group''' checkbox merges private and public IP addresses into a single column in the SIP ladder/history view. This is particularly useful for devices behind NAT (Network Address Translation) where the SIP signaling shows public IP addresses while RTP media uses private IP addresses. | ||
When enabled: | When enabled: | ||
| Line 68: | Line 76: | ||
'''Use Case Example:''' | '''Use Case Example:''' | ||
For a SIP trunk behind NAT where: | For a SIP trunk behind NAT where: | ||
* Public IP: 1.2.3.4 (appears in SIP signaling) | * Public IP: 1.2.3.4 (appears in SIP signaling) | ||
| Line 74: | Line 83: | ||
Create a group and add both IP addresses, then enable the '''SIP history group''' checkbox. The GUI will merge these into a single column in the SIP ladder view instead of showing duplicate flows. | Create a group and add both IP addresses, then enable the '''SIP history group''' checkbox. The GUI will merge these into a single column in the SIP ladder view instead of showing duplicate flows. | ||
=== Call Direction Classification | === Call Direction Classification === | ||
Using both '''Trunk''' and '''Server''' checkboxes, you can create precise CDR filter templates for differentiating inbound and outbound traffic: | Using both '''Trunk''' and '''Server''' checkboxes, you can create precise CDR filter templates for differentiating inbound and outbound traffic: | ||
| Line 80: | Line 89: | ||
* '''Outbound calls''' – Caller IP is in a '''Server''' group AND Called IP is in a '''Trunk''' group | * '''Outbound calls''' – Caller IP is in a '''Server''' group AND Called IP is in a '''Trunk''' group | ||
* '''Inbound calls''' – Caller IP is in a '''Trunk''' group AND Called IP is in a '''Server''' group | * '''Inbound calls''' – Caller IP is in a '''Trunk''' group AND Called IP is in a '''Server''' group | ||
* '''Internal calls''' – Both caller and called IPs are in (or not in) | * '''Internal calls''' – Both caller and called IPs are in the same group (or not in any group) | ||
<kroki lang="mermaid"> | |||
flowchart LR | |||
subgraph Server["Server Group (Internal)"] | |||
PBX[PBX/SBC] | |||
end | |||
subgraph Trunk["Trunk Group (External)"] | |||
Carrier[Carrier/Provider] | |||
end | |||
PBX -->|"Outbound<br/>(callerIP=Server, calledIP=Trunk)"| Carrier | |||
Carrier -->|"Inbound<br/>(callerIP=Trunk, calledIP=Server)"| PBX | |||
</kroki> | |||
==== Usage Example for Capacity Planning | ==== Usage Example for Capacity Planning ==== | ||
For generating reports showing inbound vs outbound call counts and peak concurrent calls: | For generating reports showing inbound vs outbound call counts and peak concurrent calls: | ||
| Line 89: | Line 110: | ||
# Create a '''Trunk''' group containing your carrier/provider IP ranges (enable the '''Trunk''' checkbox) | # Create a '''Trunk''' group containing your carrier/provider IP ranges (enable the '''Trunk''' checkbox) | ||
# Create CDR filter templates: | # Create CDR filter templates: | ||
#* For '''Outbound''': Select <code>callerIP</code> in your Server group AND <code>calledIP</code> in your Trunk group | |||
#* For '''Inbound''': Select <code>callerIP</code> in your Trunk group AND <code>calledIP</code> in your Server group | |||
# Generate reports using these filter templates with the "count of calls" report type | # Generate reports using these filter templates with the "count of calls" report type | ||
== Telephone Number Groups == | == Telephone Number Groups == | ||
| Line 117: | Line 129: | ||
# Add phone numbers or regex patterns one per line | # Add phone numbers or regex patterns one per line | ||
# Save the group | # Save the group | ||
==== Import/Export (Recommended for Large Lists) ==== | ==== Import/Export (Recommended for Large Lists) ==== | ||
| Line 153: | Line 150: | ||
+447911123456 | +447911123456 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== Regex Patterns in Phone Number Groups === | |||
Telephone number groups support regular expressions for pattern matching. Examples: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Pattern !! Description | |||
|- | |||
| <code>[a-zA-Z]</code> || Find numbers containing letters (malformed caller IDs) | |||
|- | |||
| <code>^500[0-9]{4}$</code> || Match specific number patterns (e.g., 5001234) | |||
|- | |||
| <code>^(\+|00)</code> || Find international numbers (starting with + or 00) | |||
|} | |||
=== Using Phone Number Groups in CDR Filters === | === Using Phone Number Groups in CDR Filters === | ||
| Line 235: | Line 247: | ||
== AI Summary for RAG == | == AI Summary for RAG == | ||
'''Summary:''' This page explains how to configure Groups (IP addresses, telephone numbers, and emails) in VoIPmonitor. IP groups support Trunk, Server, and SIP history group checkboxes: Trunk and Server checkboxes classify call direction (Outbound: callerIP in Server group and calledIP in Trunk group; Inbound: callerIP in Trunk group and calledIP in Server group); The SIP history group checkbox merges private and public IPs in the SIP ladder/history view for devices behind NAT, consolidating duplicate flows into a single display | '''Summary:''' This page explains how to configure Groups (IP addresses, telephone numbers, and emails) in VoIPmonitor. IP groups support Trunk, Server, and SIP history group checkboxes: Trunk and Server checkboxes classify call direction (Outbound: callerIP in Server group and calledIP in Trunk group; Inbound: callerIP in Trunk group and calledIP in Server group); The SIP history group checkbox merges private and public IPs in the SIP ladder/history view for devices behind NAT, consolidating duplicate flows into a single display. Telephone number groups support manual entry, import/export, and regular expression patterns for matching number ranges or specific patterns. Email groups are used for alert and report distribution. IP Anonymize Rewrite Rules allow GDPR-compliant anonymization of IP addresses in new CDR records. | ||
'''Keywords:''' groups, IP groups, telephone numbers, tel numbers, email groups, SIP trunks, alerts, filters, import, export, CDR filter, Caller Groups, Called Groups, Trunk checkbox, Server checkbox, SIP history group, inbound calls, outbound calls, internal calls, capacity planning, callerIP, calledIP, CDR filter templates, IP anonymize, rewrite rules, GDPR, privacy, IP masking, network anonymization, NAT, network address translation, SIP ladder, SIP history view, duplicate flows, private IP, public IP | '''Keywords:''' groups, IP groups, telephone numbers, tel numbers, email groups, SIP trunks, alerts, filters, import, export, CDR filter, Caller Groups, Called Groups, Trunk checkbox, Server checkbox, SIP history group, inbound calls, outbound calls, internal calls, capacity planning, callerIP, calledIP, CDR filter templates, IP anonymize, rewrite rules, GDPR, privacy, IP masking, network anonymization, NAT, network address translation, SIP ladder, SIP history view, duplicate flows, private IP, public IP, regex patterns, regular expressions, number filtering, GUI refresh, login refresh | ||
'''Key Questions:''' | '''Key Questions:''' | ||
| Line 246: | Line 258: | ||
* What is the SIP history group checkbox used for? | * What is the SIP history group checkbox used for? | ||
* How do I merge private and public IPs in the SIP ladder view for NAT devices? | * How do I merge private and public IPs in the SIP ladder view for NAT devices? | ||
* How do I differentiate inbound and outbound calls for capacity planning? | * How do I differentiate inbound and outbound calls for capacity planning? | ||
* How do I create CDR filter templates using IP groups? | * How do I create CDR filter templates using IP groups? | ||
* How do I import a large list of phone numbers into a group? | * How do I import a large list of phone numbers into a group? | ||
* How do I filter CDRs by a group of phone numbers? | * How do I filter CDRs by a group of phone numbers? | ||
* Can I use regular expressions in telephone number groups? | |||
* How do I configure IP anonymize rewrite rules for GDPR compliance? | * How do I configure IP anonymize rewrite rules for GDPR compliance? | ||
* Why is my new group not visible in dropdown lists after creating it? | |||
* Why is my new | |||
* Do I need to refresh the GUI after creating a new group? | * Do I need to refresh the GUI after creating a new group? | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 6 January 2026
Groups define sets of IP addresses/networks, telephone numbers/prefixes, and emails. These can be used across the WEB GUI for filtering CDRs, configuring alerts, and other features. Groups allow you to manage large collections of identifiers efficiently and reuse them across multiple configurations.
Overview
VoIPmonitor supports three types of groups:
| Group Type | Use Cases | Access Path |
|---|---|---|
| IP Groups | Define SIP trunks, filter by source/destination IP, distinguish internal/external calls | GUI → Groups → IPs |
| Telephone Number Groups | Filter CDRs by caller/called numbers, alert on specific number ranges | GUI → Groups → Tel. numbers |
| Email Groups | Define recipients for alerts and reports | GUI → Groups → Emails |
Important: GUI Refresh Required
After creating a new group (IP, telephone number, or email), the group may not immediately appear in dropdown lists used throughout the GUI (such as CDR filter templates, alert configurations, or charts). This is because the GUI loads available groups at login time.
Solution:
- Log out of the GUI
- Log back in
- The newly created group will now appear in all relevant dropdowns
This applies to all group types when used in:
- CDR filter templates (Caller Groups, Called Groups dropdowns)
- Alert configurations
- Charts filters
- Any other GUI component that uses groups
IP Groups
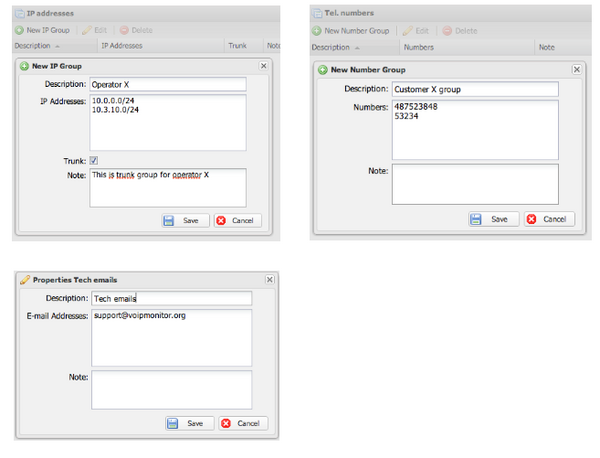
IP Groups allow you to define sets of IP addresses or network ranges that can be used in CDR filters and alerts.
Creating IP Groups
- Navigate to GUI → Groups → IPs
- Click "New group"
- Enter a descriptive group name (e.g., "Provider A SIP Trunk" or "Internal PBX Servers")
- Add IP addresses or CIDR ranges, one per line
- Configure the Trunk, Server, or SIP history group checkboxes as applicable (see below)
- Save the group
Example IP Group Entries
192.168.1.100
10.0.0.0/24
172.16.0.0/16
2001:db8::1/128
Trunk Checkbox
The Trunk checkbox marks the IPs in this group as belonging to an external SIP trunk (e.g., your VoIP provider or carrier).
Server Checkbox
The Server checkbox marks IPs in this group as belonging to your internal PBX servers or VoIP infrastructure. This is used in conjunction with the Trunk checkbox to accurately classify call direction.
SIP History Group Checkbox
The SIP history group checkbox merges private and public IP addresses into a single column in the SIP ladder/history view. This is particularly useful for devices behind NAT (Network Address Translation) where the SIP signaling shows public IP addresses while RTP media uses private IP addresses.
When enabled:
- The GUI treats all IPs in this group as belonging to the same logical endpoint
- Duplicate flows showing both private and public IPs are consolidated into a single display
- Call flows in the SIP History tab become easier to read and analyze
Use Case Example:
For a SIP trunk behind NAT where:
- Public IP: 1.2.3.4 (appears in SIP signaling)
- Private IP: 10.0.0.3 (actual device IP)
Create a group and add both IP addresses, then enable the SIP history group checkbox. The GUI will merge these into a single column in the SIP ladder view instead of showing duplicate flows.
Call Direction Classification
Using both Trunk and Server checkboxes, you can create precise CDR filter templates for differentiating inbound and outbound traffic:
- Outbound calls – Caller IP is in a Server group AND Called IP is in a Trunk group
- Inbound calls – Caller IP is in a Trunk group AND Called IP is in a Server group
- Internal calls – Both caller and called IPs are in the same group (or not in any group)
Usage Example for Capacity Planning
For generating reports showing inbound vs outbound call counts and peak concurrent calls:
- Create a Server group containing your internal PBX/server IP ranges (enable the Server checkbox)
- Create a Trunk group containing your carrier/provider IP ranges (enable the Trunk checkbox)
- Create CDR filter templates:
- For Outbound: Select
callerIPin your Server group ANDcalledIPin your Trunk group - For Inbound: Select
callerIPin your Trunk group ANDcalledIPin your Server group
- For Outbound: Select
- Generate reports using these filter templates with the "count of calls" report type
Telephone Number Groups
Telephone number groups allow you to define sets of phone numbers or prefixes that can be used in CDR filters, alerts, and other parts of the GUI.
Creating and Managing Phone Number Groups
You can create phone number groups manually one at a time, or use the import/export functionality for large lists. Telephone number groups support both explicit numbers and regular expression patterns.
Manual Entry
- Navigate to GUI → Groups → Tel. numbers
- Click the "New group" button
- Enter a Group name
- Add phone numbers or regex patterns one per line
- Save the group
Import/Export (Recommended for Large Lists)
The import/export feature allows you to create and manage large lists of phone numbers efficiently.
To import phone numbers:
- Navigate to GUI → Groups → Tel. numbers
- Click the "import/export" button
- Prepare a text file with one phone number per line (or use the exported file as a template)
- Upload the file
- The list will be imported into a new or existing group
Example import file:
+12025551234
+12025551235
+12025551236
+447911123456
Regex Patterns in Phone Number Groups
Telephone number groups support regular expressions for pattern matching. Examples:
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
[a-zA-Z] |
Find numbers containing letters (malformed caller IDs) |
^500[0-9]{4}$ |
Match specific number patterns (e.g., 5001234) |
| 00) | Find international numbers (starting with + or 00) |
Using Phone Number Groups in CDR Filters
After creating a phone number group:
- Go to the CDR view
- Click the "Filter Form" button
- In the Common tab, locate the "Group Filters" section
- Select your group from the "Caller Groups" or "Called Groups" dropdown
- Click "Search"
Benefits of using groups:
- Any changes made to the group are automatically propagated to all filters where the group is used
- Ideal for managing large lists of phone numbers
- Groups can be reused across multiple filters and alerts
Maximum Limits
The Caller/Called manual entry fields in the CDR filter form are designed for small lists. For large lists of phone numbers, using groups with the import/export functionality is the recommended approach to ensure stability and maintainability.
Email Groups
Email groups define sets of email addresses for use in alerts and reports.
Creating Email Groups
- Navigate to GUI → Groups → Emails
- Click "New group"
- Enter a group name (e.g., "NOC Team", "Management")
- Add email addresses, one per line
- Save the group
Using Email Groups
Email groups can be used in:
- Alerts – Send notifications to a group of recipients
- Reports – Distribute scheduled reports to multiple addresses
IP Anonymize Rewrite Rules
This feature replaces original IP addresses in the database with anonymized values. It is useful for privacy compliance (GDPR) or hiding internal network topology.
Configuration Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Description | Name of the rule. |
| IP to anonymize | The original IP or network range you want to hide. |
| Mask [0-32] | Source CIDR mask (e.g., 32 for a single IP, 24 for a whole subnet). |
| Anonymous IP | The new IP address that will be stored in the database. |
| Mask [0-32] | Target mask. If this matches the source mask, the host part of the IP is preserved (1:1 mapping). |
Example: Network Prefix Anonymization
To hide the real network prefix (e.g., 192.168.1.x) but keep the host addresses unique (mapping 192.168.1.55 → 10.0.0.55):
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| IP to anonymize | 192.168.1.0 |
| Mask | 24 |
| Anonymous IP | 10.0.0.0 |
| Mask | 24 |
Note: These rules apply only to new data processed after saving the configuration. Existing records in the database are not retroactively anonymized.
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: This page explains how to configure Groups (IP addresses, telephone numbers, and emails) in VoIPmonitor. IP groups support Trunk, Server, and SIP history group checkboxes: Trunk and Server checkboxes classify call direction (Outbound: callerIP in Server group and calledIP in Trunk group; Inbound: callerIP in Trunk group and calledIP in Server group); The SIP history group checkbox merges private and public IPs in the SIP ladder/history view for devices behind NAT, consolidating duplicate flows into a single display. Telephone number groups support manual entry, import/export, and regular expression patterns for matching number ranges or specific patterns. Email groups are used for alert and report distribution. IP Anonymize Rewrite Rules allow GDPR-compliant anonymization of IP addresses in new CDR records.
Keywords: groups, IP groups, telephone numbers, tel numbers, email groups, SIP trunks, alerts, filters, import, export, CDR filter, Caller Groups, Called Groups, Trunk checkbox, Server checkbox, SIP history group, inbound calls, outbound calls, internal calls, capacity planning, callerIP, calledIP, CDR filter templates, IP anonymize, rewrite rules, GDPR, privacy, IP masking, network anonymization, NAT, network address translation, SIP ladder, SIP history view, duplicate flows, private IP, public IP, regex patterns, regular expressions, number filtering, GUI refresh, login refresh
Key Questions:
- What types of groups are available in VoIPmonitor?
- How do I create an IP group for a SIP trunk?
- What is the Trunk checkbox and how does it affect call classification?
- What is the Server checkbox and when should I use it?
- What is the SIP history group checkbox used for?
- How do I merge private and public IPs in the SIP ladder view for NAT devices?
- How do I differentiate inbound and outbound calls for capacity planning?
- How do I create CDR filter templates using IP groups?
- How do I import a large list of phone numbers into a group?
- How do I filter CDRs by a group of phone numbers?
- Can I use regular expressions in telephone number groups?
- How do I configure IP anonymize rewrite rules for GDPR compliance?
- Why is my new group not visible in dropdown lists after creating it?
- Do I need to refresh the GUI after creating a new group?