Silence detection: Difference between revisions
(Add section explaining how to use silence detection for identifying calls with background noise and differentiating between caller/called party noise) |
(Review: fix table cell separators (|| instead of |)) |
||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
! Audio Environment !! Silence Detection Behavior !! Typical Silence % Range | ! Audio Environment !! Silence Detection Behavior !! Typical Silence % Range | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Clean / quiet office | Normal silence during pauses | 40-70% | | Clean / quiet office || Normal silence during pauses || 40-70% | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Environmental noise (air conditioning, distant voices) | Partial detection | 10-39% | | Environmental noise (air conditioning, distant voices) || Partial detection || 10-39% | ||
|- | |- | ||
| High noise (factory floor, crowded call center) | Almost no silence detected | 0-9% | | High noise (factory floor, crowded call center) || Almost no silence detected || 0-9% | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 21:28, 6 January 2026
This guide explains how to enable and use VoIPmonitor's advanced audio analysis features for G.711 codecs, including silence detection and audio clipping detection. These tools are invaluable for diagnosing audio quality issues that are not caused by network packet loss, such as one-way audio, muted microphones, or faulty endpoint hardware.
Overview & Use Cases
Standard network metrics like packet loss and jitter can only identify problems that occur during network transport. However, many audio quality issues originate at the endpoint itself. The Silence & Clipping Detection engine analyzes the decoded G.711 (a-law/u-law) audio stream to identify these problems.
Enable this feature to diagnose issues like:
- A user complaining about "dead air" when the network statistics look perfect
- One-way audio scenarios where one party is not transmitting any sound
- Identifying calls with audio clipping, which is often perceived as clicks or distortion
- More accurately assessing call quality by penalizing MOS scores for periods of absolute silence
- Detecting calls in noisy environments - using silence threshold to identify calls with background noise (see Noise Detection Workflow below)
Prerequisites
Before enabling this feature, please ensure the following requirements are met:
- 1. Codec Limitation
- This feature currently only supports calls using the G.711 a-law/u-law codec. Audio streams from other codecs will not be analyzed.
- 2. CPU Resources
- Decoding and analyzing audio streams is a CPU-intensive process. Enabling these features will increase the overall CPU load on the sensor. Monitor your system's performance after enabling them.
- 3. Database Schema
- All modern VoIPmonitor installations (approximately since 2020) include the necessary database columns by default. If you are running a current version, you do not need to perform any database modifications. The sensor will log an error on startup if any required columns are missing, which should only happen on very old legacy systems.
Configuration
Step 1: Enable in voipmonitor.conf
To activate the features, add or uncomment the following lines in /etc/voipmonitor.conf:
# Enables both silence and clipping detection logic
silencedetect = yes
# Enables the specific feature that detects clipped audio frames
clippingdetect = yes
# Defines the audio level threshold for silence. The default of 512 is
# tolerant to low-level background noise. Lower values are stricter.
silencethreshold = 512
After making changes, restart the voipmonitor service:
systemctl restart voipmonitor
Step 2: For Legacy Upgrades - Adding Database Columns
Note: This step is only required if you are upgrading from a very old VoIPmonitor installation and the sensor logs errors about missing columns on startup. For all recent installations, these columns already exist.
If required, you can add the columns to your cdr table with the following SQL command. Only add the columns that are reported as missing.
ALTER TABLE cdr
ADD COLUMN caller_silence tinyint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN called_silence tinyint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN caller_silence_end smallint default NULL,
ADD COLUMN called_silence_end smallint default NULL,
ADD COLUMN caller_clipping_div3 smallint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN called_clipping_div3 smallint unsigned default NULL,
ADD COLUMN a_mos_silence_min_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
ADD COLUMN b_mos_silence_min_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
ADD COLUMN a_mos_silence_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
ADD COLUMN b_mos_silence_mult10 tinyint unsigned DEFAULT NULL;
Features & Metrics
Once enabled, you will have access to several new metrics and visualizations throughout the GUI.
1. Silence as Packet Loss & MOS Adjustment
The system identifies frames of absolute silence (e.g., from a muted mic) and treats them as a form of packet loss. This allows VoIPmonitor to correctly calculate a low MOS score for calls that were silent, even if no actual packets were lost on the network.
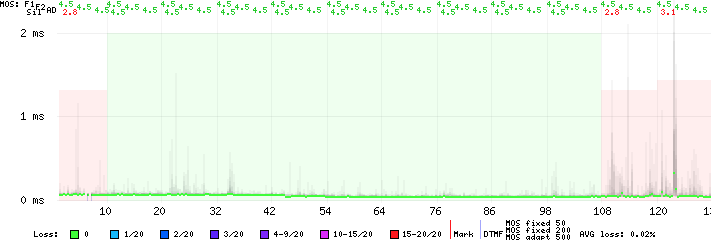
This is visualized in the CDR Graph Detail, where a new MOS score labeled "Sil" (Silence MOS) will appear.
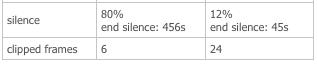
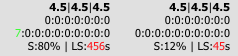
2. Overall Silence Percentage
The CDR Detail view will show the total percentage of silence for both the caller and callee audio streams. A call with over 95% silence in one direction is a strong indicator of a one-way audio problem.
3. Silence at the End of a Call
This metric measures the duration of silence leading up to the end of the call. A high value may indicate that a user hung up out of frustration because they couldn't hear the other party. This value is shown directly in the main CDR listing.
4. Audio Clipping Detection
The system counts the number of "clipped" audio frames, which occur when the audio signal is too loud and hits the maximum amplitude, causing distortion. This metric is shown in the CDR detail and can be used for filtering and creating charts to find problematic endpoints.
5. MOS Scores During Silence Periods
When silence detection is enabled, VoIPmonitor calculates additional MOS values that appear after the standard MOS scores in the CDR table. These values represent the voice quality specifically during periods of silence in the call.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
a_mos_silence_mult10 / b_mos_silence_mult10 |
Average MOS score during silence periods (caller/callee) |
a_mos_silence_min_mult10 / b_mos_silence_min_mult10 |
Minimum MOS score during silence periods (caller/callee) |
Important Notes:
- These metrics are only active when silence detection is enabled (
silencedetect = yes) - If silence detection is disabled, the system shows the full/regular MOS score instead
- These values help identify calls where audio quality deteriorates during silent periods, which may indicate endpoint problems
6. Detecting Calls with Background Noise
You can use the silence detection feature to identify calls occurring in noisy environments (e.g., call centers with background chatter, factories with machinery, or offices with environmental noise). This works because calls with background noise are not registered as silent - the continuous audio above the threshold prevents silence detection from triggering.
How it works:
| Audio Environment | Silence Detection Behavior | Typical Silence % Range |
|---|---|---|
| Clean / quiet office | Normal silence during pauses | 40-70% |
| Environmental noise (air conditioning, distant voices) | Partial detection | 10-39% |
| High noise (factory floor, crowded call center) | Almost no silence detected | 0-9% |
Workflow to identify noisy environments:
1. Configure silencedetect = yes and silencethreshold = 512 (or appropriate level for your environment)
2. Identify sample calls from different environments:
* Calls from "clean" offices (e.g., administrative staff, IT department) * Calls from "noisy" locations (e.g., sales floor with headset chatter, manufacturing site)
3. Compare the caller_silence and called_silence percentages in the CDR:
* Use the CDR filter to showCaller Silence < 20%ORCalled Silence < 20%* This will display calls with continuous audio (potential background noise)
4. Analyze the audio recordings of these low-silence calls to confirm the presence of noise
5. Create saved filters or alerts for systematic monitoring
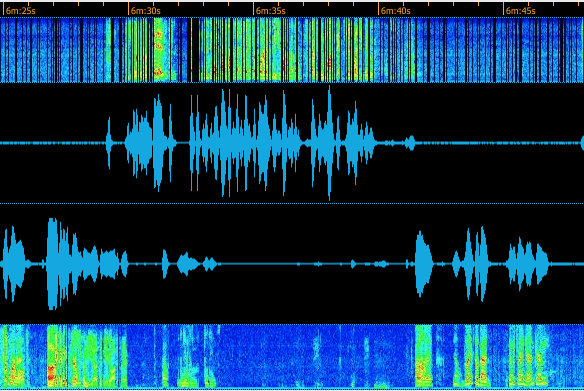
Tip: Use the spectral analysis view in CDR Graph Detail to visually distinguish between:
- White/brown noise (continuous frequency spectrum - machinery, air conditioning)
- Sporadic noise (intermittent - voices, doors slamming, equipment beeps)
- Genuine speech (natural frequency patterns with pauses for silence)
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: VoIPmonitor's Silence and Clipping Detection analyzes G.711 (a-law/u-law) audio to diagnose issues invisible to network metrics. Key features: treats silence as packet loss for accurate MOS, calculates silence percentage (>95% indicates one-way audio), measures end-of-call silence, counts clipped frames, and detects calls with background noise (low silence %). Configuration requires silencedetect=yes and clippingdetect=yes in voipmonitor.conf. Modern installations have required database columns by default.
Keywords: silence detection, clipping, one-way audio, dead air, MOS, G.711, silencedetect, clippingdetect, silencethreshold, mos_silence, background noise, noisy environments
Key Questions:
- How can I diagnose one-way audio problems?
- Why is a call's MOS score high even though the user reported hearing nothing?
- How does VoIPmonitor detect silence in a call?
- What does the "Silence MOS" score mean in the CDR graph?
- How can I find calls with audio clipping?
- How can I filter calls based on background noise and differentiate between caller and called party noise?