Settings
Category:GUI manual
This page documents the configuration options available in the VoIPmonitor web GUI under the Settings menu. These settings control how the GUI interacts with sensors, displays data, and manages user preferences.
Sensors
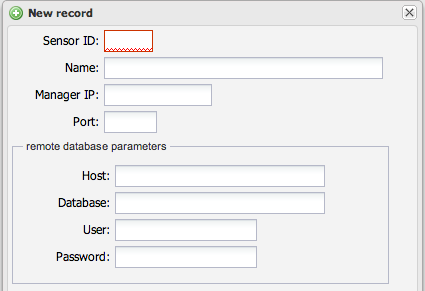
If id_sensor is set in /etc/voipmonitor.conf (default is blank), you must create sensor entries here to enable downloading files like PCAP, graphs, and WAV recordings from the GUI.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensor ID | The numeric ID matching id_sensor = N in voipmonitor.conf
|
| Name | A descriptive name for the sensor |
| Manager IP | IP address of the sensor for fetching data (PCAP, graph, audio files) |
| Manager Port | TCP port for the manager API (default: 5029) |
| Remote database | Database connection parameters for "Legs by CID/header" lookups when sensors use different databases. Leave blank if all sensors share the same database. |
SSL/TLS Configuration
Sensors can be configured to decrypt TLS-encrypted SIP traffic directly through the GUI. This is particularly useful when VoIPmonitor is not capturing all SIP traffic from specific TLS trunks (e.g., seeing only OPTIONS and 403 responses while INVITEs are missing).
To configure SSL/TLS settings for a sensor:
- Navigate to Settings > Sensors
- Click the wrench icon next to the affected sensor
- In the search field at the top right of the sensor settings dialog, enter ssl_
- Configure the required SSL/TLS parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| ssl_key | Path to the private key file (PEM format) for decrypting TLS traffic | /etc/pki/tls/private/server.key
|
| ssl_cert | Path to the SSL certificate file (PEM format) matching the private key | /etc/pki/tls/certs/server.crt
|
| ssl_ipport | IP address and TLS port of the SIP endpoint to decrypt (without key file path for SSL Key Logger mode, or IP:port /path/to/key for Private Key mode) |
192.168.1.10:5061
|
| ssl | Enable SSL/TLS decryption module on the sensor | yes
|
Important Notes:
- The sensor SSL settings correspond to the configuration parameters in /etc/voipmonitor.conf but are managed through the GUI interface
- This is an alternative to editing
voipmonitor.confdirectly - the GUI applies these settings to the sensor - After changing SSL settings, you may need to restart the sniffer service or use the "reload sniffer" button in the GUI control panel
- For decryption of traffic using Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) ciphers like Diffie-Hellman (DHE/ECDHE), see the TLS decryption guide for the SSL Key Logger method
When to use GUI SSL configuration:
- You prefer managing TLS/SSL settings through the web interface instead of editing config files
- You have multiple sensors and want to manage SSL keys centrally
- You need to quickly enable/disable TLS decryption without editing
voipmonitor.conf
For detailed information on TLS decryption methods and limitations (including PFS ciphers), see Tls.
Sensor Health Monitoring with RRD Charts
If you experience poor call quality (low MOS scores, choppy playback) and need to determine whether the issue is network-related or caused by the sniffer host being overloaded, use the RRD (Round Robin Database) charts available in the GUI.
- Accessing Sensor RRD Charts:**
- Navigate to Settings > Sensors
- Locate the sensor you want to monitor
- Click the chart icon next to the sensor entry
- This opens the RRD performance graphs for that sensor
- Key Metrics to Check:**
| Metric | Description | What It Indicates |
|---|---|---|
| Buffer usage | Shows the percentage of available packet buffer being used | Sensor is approaching capacity limits if consistently high |
| Packet drops | Counts of packets the sensor could not process | Sensor is overloaded and dropping packets due to high traffic load |
- Interpreting the Charts:**
If you observe:
- Buffer usage growing to 100% and remaining at maximum capacity
- Packet drops being recorded (non-zero values on the packet drops graph)
This indicates the sniffer host is overloaded and is the source of audio quality issues. The sensor cannot keep up with incoming packet rate, causing packets to be dropped before they can be processed and stored. This results in:
- Low MOS scores
- Choppy audio playback in the GUI
- Missing call data
- Solutions for Sensor Overload:**
- Increase the kernel packet ring buffer size in
voipmonitor.conf:ringbuffer = 200(default: 50, recommended: >= 500 for >100 Mbit traffic). This allows the operating system to buffer more packets before they are passed to VoIPmonitor, reducing kernel-level packet drops. - Add more sensors to distribute the load (Distributed Architecture)
- Use specialized capture hardware (DPDK, Native Napatech cards, PF_RING)
- Reduce capture scope (more restrictive capture rules)
- Upgrade sensor hardware (faster CPU, more RAM)
- Reduce PCAP file storage or enable compression
- When to Check RRD Charts:**
Use RRD charts to diagnose sensor overload when:
- Other platforms show clear audio but VoIPmonitor shows poor quality
- Only the sniffer host is affected, not the actual VoIP network
- Performance log shows high packet drops or buffer saturation
This diagnostic step helps distinguish between network quality issues (jitter, loss in the actual VoIP path) vs. sniffer capacity issues (capturing host overload).
Troubleshooting: Non-deletable Local Sensor
In server/probe deployments where the GUI server is not sniffing traffic itself, a "local sensor" may be automatically created in the sensor list. This sensor cannot be deleted through the normal GUI interface.
Workaround:
- In Settings > Sensors, add a new sensor with the same Sensor ID, name, and settings as the non-deletable local sensor
- After saving, the original automatically created sensor should either disappear or become deletable
- You can then remove the duplicate entry if both sensors appear
This occurs because the GUI automatically creates a sensor entry when it detects that id_sensor is set in the configuration but no active capture is configured on the GUI host.
Troubleshooting: Server Instance Not Appearing in GUI
After replacing a server/SBC and reusing its IP address, the server instance may disappear from the GUI sensor list, even though it is sending data and appears in CDRs with a warning.
Problem: Sensor Appears in CDRs With Warning But Not in GUI List
When you replace hardware (server, SBC, sensor host) but reuse the same IP address, the GUI may not automatically rediscover the server instance. CDRs from the new device appear in the database, but:
- The server instance is not visible in Settings > Sensors
- CDR records contain a warning about unknown sensor or manager connection
- The new server is working but not properly registered with the GUI
Solution: Manually Create Server Instance Entry
If your deployment uses server instances that connect directly to the MySQL database, follow these steps:
Step 1: Create the server instance entry in the GUI
- Navigate to Settings > Sensors
- Click Add new sensor or New sensor
- Configure the following fields:
- Sensor ID: Enter a unique identifier (e.g.,
2) - Name: Descriptive name for the server instance (e.g.,
SBC-Production) - Manager IP: IP address of the server instance (the new hardware's IP)
- Manager Port: TCP port for the manager connection (default:
5029)
- Sensor ID: Enter a unique identifier (e.g.,
Step 2: Configure managerip and managerport on the server instance
Edit the voipmonitor.conf file on the new server instance to point to the GUI:
# On the new server instance (/etc/voipmonitor.conf)
managerip = gui.server.ip # GUI server IP address
managerport = 5029 # Manager API port (matches GUI Manager Port)
Restart the voipmonitor service after making changes:
systemctl restart voipmonitor
Step 3: Verify network connectivity
Ensure bidirectional network connectivity:
- GUI host → Server instance: GUI must be able to reach the server instance on the configured Manager IP/Port (for data retrieval and control)
- Server instance → MySQL database: Server instance must be able to write CDRs to the MySQL database
Test connectivity from both directions:
# From GUI host to server instance (verify Manager IP/Port)
nc -zv server.instance.ip 5029
# From server instance to MySQL database
mysql -h mysql.server.ip -u voipmonitor -p voipmonitor -e "SELECT 1"
Check firewall rules on both systems to ensure:
- TCP/5029 (Manager port) is allowed from GUI to server instance
- MySQL port (usually 3306) is allowed from server instance to database
Step 4: Verify server instance status
After configuration, the server instance should appear in Settings > Sensors with a green status indicating it is connected. Any probes or sniffing interfaces connected to that server instance will be automatically discovered and listed under the server instance in the sensor tree.
Alternative: Using Modern Client-Server Mode
If you are planning a new deployment or can reconfigure your architecture, consider using the modern Client-Server mode which provides:
- Encrypted TCP connections between sensors and central server
- Automatic sensor registration (no manual GUI entry required)
- Simplified firewall configuration (single port: 60024 by default)
In Client-Server mode, sensors connect to a central server using server_destination and server_destination_port, and the central server handles SQL database writes. Sensors do not need direct MySQL database access.
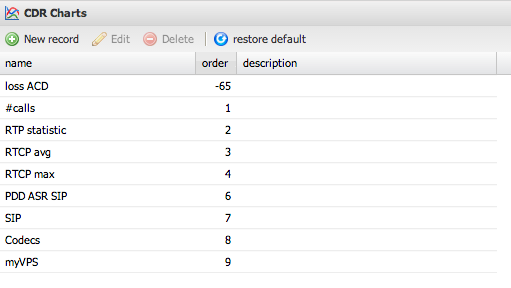
CDR Charts
This section allows you to define predefined charts that appear in the CDR detail view's Charts tab. These charts provide quick visual analysis for specific call records based on caller/called information.
CDR Custom Headers
Since sniffer version 7.0RC7, VoIPmonitor can store custom SIP headers in the database for viewing and searching in the GUI. For the sniffer configuration, see Sniffer_configuration#custom_headers.
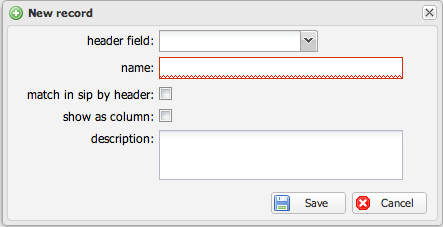
Configuration Fields
- Header Field
- Combo box listing available headers from the
cdr_next.custom_header*database columns. These are automatically created when you add headers tocustom_headersinvoipmonitor.confand restart the sniffer.
- Name
- The display name for this header in the CDR view header panel.
- Match in SIP by Header
- When enabled, this header is used for matching CDRs in the Legs by header tab. This is useful when you have a unique correlation identifier that links multiple call legs (e.g., from phone to SBC, and from SBC to provider). Alternative method: matchheader in voipmonitor.conf.
- Show as Column
- When enabled, displays this header as a column in the CDR list view.
Apply Configuration Changes
Important: Restart Required
After configuring or modifying custom header settings in the GUI, you must restart the sensor service for the changes to take effect. The restart applies the new configuration so that the sensor begins capturing and storing custom SIP headers as specified.
To restart the sensor:
# Using systemd
systemctl restart voipmonitor
# Using init scripts
/etc/init.d/voipmonitor restart
After restarting, generate new test calls to verify that the custom header is being captured and stored correctly in the database.
Filtering Custom Headers
After configuring custom headers in the GUI, they appear in the CDR filter form where you can search for them using special values:
- Find all CDRs with this header present: Use the
%wildcard as the filter value. This matches any non-empty value. - Find all CDRs without this header: Type
NULL(or leave empty) as the filter value to find calls where this header was not present. - Specific value search: Enter the exact header value (or use
%as a wildcard for partial matches, e.g.,sip:%to find SIP URIs).
These filters appear in the CDR filter form after you have processed at least one call containing the custom header.
Limitations
The GUI custom header feature has the following limitations:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| No Regexp extraction | Custom headers store the complete raw header value. There is no option to extract portions using regular expressions (e.g., extracting just an IP address from a SIP URI). |
| No Delimiter aggregation | If a SIP header appears multiple times in a message (e.g., multiple Contact headers in a SIP 300 response), only one value is stored. Controlled by custom_headers_last_value in voipmonitor.conf (first or last occurrence).
|
| No per-method filtering | Custom headers are captured from all SIP messages. There is no option to capture only from specific SIP methods (INVITE, BYE, etc.) or response codes (200, 300, etc.). |
For advanced header extraction needs, contact VoIPmonitor support to discuss custom development or alternative approaches such as external PCAP processing.
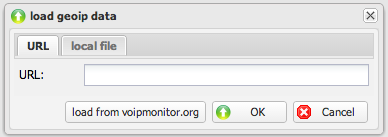
Load GeoIP Data
Loads GeoIP data into the internal database for the CDR detail Map tab, which displays geographic locations of call participants.
System Configuration
The System Configuration section contains core settings that affect the overall behavior of the GUI.
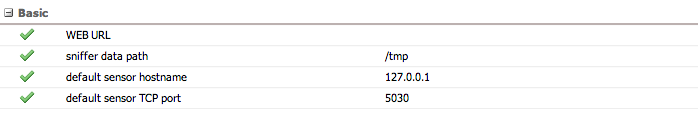
Basic
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| WEB URL | Base URL for the GUI, used in hypertext links (e.g., in email alerts) |
| Sniffer data path | Directory where sniffer stores data (default: /var/spool/voipmonitor)
|
| Default sensor hostname | Default hostname for connecting to the sniffer (default: localhost). For multiple sensors, configure them in Settings > Sensors |
| Default sensor TCP port | Default TCP port for the manager API (default: 5029) |
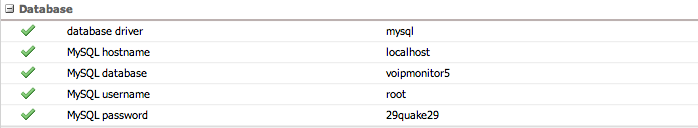
Database
Configuration for the MySQL/MariaDB database connection used by the GUI.
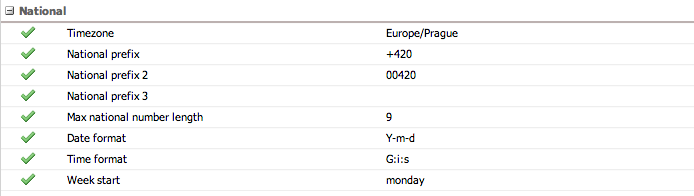
National
Settings for localizing call classification and date/time display formats.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Timezone | Server timezone (format: Country/City, e.g., Europe/Prague) |
| National prefix, 2, 3 | Prefixes used to classify calls as national vs. international (used in Active calls view) |
| Max national number length | Numbers longer than this are classified as international regardless of prefix |
| Date format | PHP date format string (default: Y-m-d). See PHP DateTime format
|
| Time format | PHP time format string (default: G:i:s). See PHP DateTime format
|
| Week start | First day of the week for calendar displays |
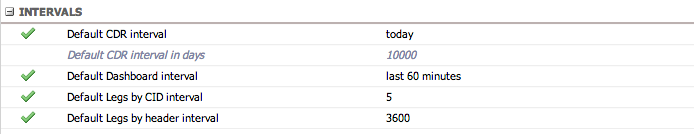
Intervals
Default time intervals for various GUI views and filters.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Default CDR interval | Default time filter when entering the CDR section. If set to "specified number of days", configure in the next option |
| Default CDR interval in days | Number of days for the CDR filter (only editable if above is set to "specified number of days") |
| Default dashboard interval | Default time filter when entering the dashboard |
| Default Legs by CID interval | Time window (+/-) for finding related calls in the Legs by CID tab (default: 5 seconds) |
| Default Legs by header interval | Time window (+/-) for finding related calls in the Legs by header tab (default: 5 seconds) |
Email / HTTP Referer
Email configuration settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| DEFAULT_EMAIL_FROM | Default "From" address for outgoing emails |
| Disable email plain text | Enable to force HTML-only emails. Useful for mail clients that display only plain text incorrectly (e.g., older Outlook versions) |
License
License and notification email configuration.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| License email | Email address for receiving license issue and overage notification emails |
Disabling License Notification Emails:
To stop receiving license issue and overage notification emails:
- Navigate to Settings > License
- Remove the email address from the "License email" field
- Save the changes
Note: This only disables license-related notification emails. Other automated emails (QoS alerts, daily reports, sensor health alerts) will continue to function.
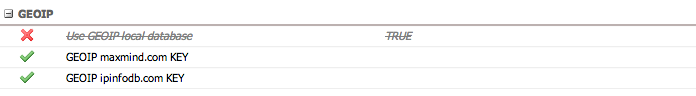
GeoIP
Configuration for GeoIP services used in the CDR Map view.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Use GeoIP local database | Enable/disable the internal GeoIP database (if loaded via Load GeoIP Data) |
| GeoIP maxmind.com KEY | API key for MaxMind GeoIP service |
| GeoIP ipinfodb.com KEY | API key for IPInfoDB service |
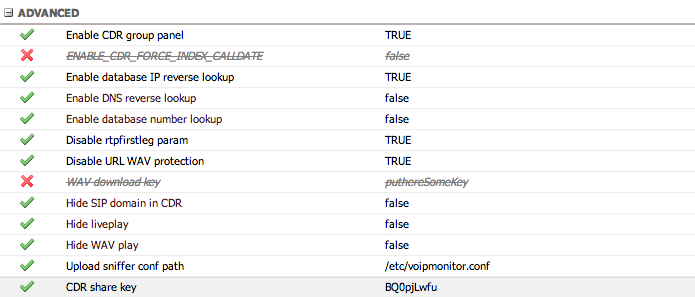
Advanced
Advanced configuration options for power users and specific use cases.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable CDR group panel | Show/hide the group panel at the bottom of the CDR view |
| ENABLE_CDR_FORCE_INDEX_CALLDATE | Force use of the calldate index on CDR queries. Enable only for unoptimized MySQL installations experiencing slow queries |
| Enable database IP reverse lookup | Resolve IP addresses to names using the internal IP lookup table |
| Enable DNS reverse lookup | Resolve IP addresses to names using DNS |
| Enable database number lookup | Resolve phone numbers to names using the internal prefix lookup table |
| Disable rtpfirstleg param | Disable the --rtp-firstleg parameter for PCAP audio decoding. Enable only if experiencing audio issues
|
| Disable URL wav protection | Skip session authentication for WAV file downloads. Use with WAV download key for secure external access |
| WAV download key | Secret key required for WAV downloads when URL protection is disabled |
| Hide SIP domain in CDR | Hide SIP domains in the CDR display |
| Hide live play | Hide live playback buttons in Active calls |
| Hide WAV play | Hide WAV playback buttons in CDR view |
| Upload sniffer conf path | Path to voipmonitor.conf for PCAP upload functionality |
| CDR share key | Secret string used to generate unique hashes for CDR share URLs |
| Folder for export CSV | Directory where CSV files from crontab scheduler tasks are saved |
| CSV name prefix | Optional prefix for CSV filenames generated by crontab tasks |
| Delete CSV after X days | Auto-delete CSV files older than specified days |
| Pcap deduplication before download | Enable to remove duplicate and retransmitted SIP/RTP packets when downloading PCAP files from the GUI. This may cause a mismatch between the packet count shown in the GUI SIP History and the packet count in the downloaded PCAP file. Disable to ensure the downloaded PCAP contains all captured packets including duplicates |
| Http proxy (for upgrades) | Proxy server address and port for automatic GUI and sniffer upgrades via the web interface. Required when the VoIPmonitor server is behind a corporate firewall or proxy and cannot connect directly to download.voipmonitor.org or github.com. Format: http://proxy-server-ip:port or http://username:password@proxy-server-ip:port for authenticated proxies
|
Troubleshooting: GUI Upgrades Behind Proxy Servers
If the GUI or sensor upgrade process fails due to network restrictions or firewall blocking direct internet access:
Solution 1: Configure HTTP Proxy in GUI (Recommended)
- Navigate to Settings > System Configuration > Advanced
- Find the Http proxy (for upgrades) field
- Enter your proxy server address:
http://proxy-server-ip:port - If authentication is required, include credentials:
http://username:password@proxy-server-ip:port - Save the settings
- Retry the GUI upgrade (Settings > System > Upgrade) or sensor upgrade (Settings > Sensors)
Solution 2: Proxy for Remote Sensors (curlproxy)
For remote sensors that need to download packages independently, configure the curlproxy parameter directly on the sensor:
- SSH into the remote sensor server
- Edit the sensor configuration:
sudo nano /etc/voipmonitor.conf - Add or modify the
curlproxyline in the[general]section:
[general]
curlproxy = http://proxy-server-ip:port
- Restart the sensor service:
sudo systemctl restart voipmonitor - Retry the upgrade from the GUI (Settings > Sensors)
References:
Localization
Create custom translations for the GUI interface. Localizations are not 100% complete; please report missing translation items.
- Red numbers indicate untranslated items, which is useful after upgrading to identify new strings
- Changes take effect after logout/login
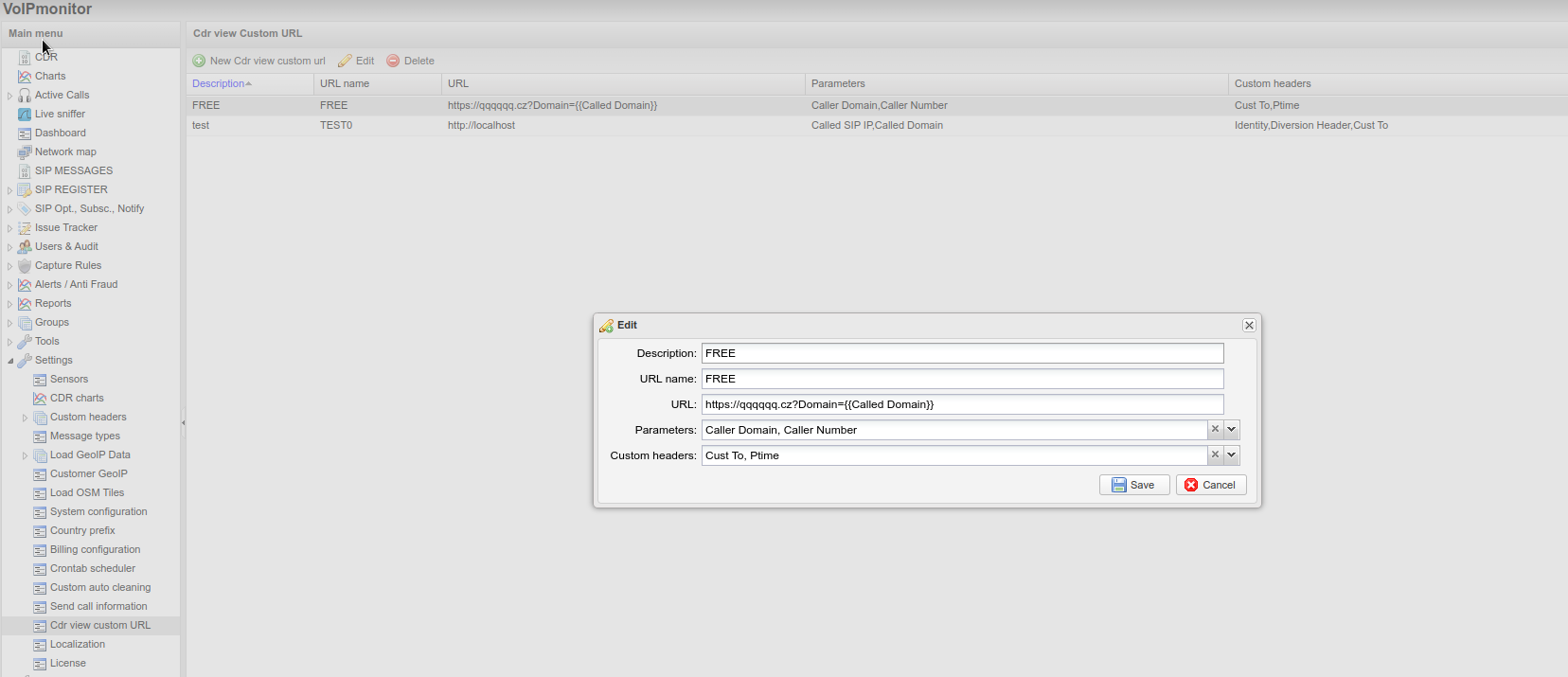
CDR View Custom URL
Add custom hyperlinks to the CDR view Commands column. This is useful for integrating external monitoring or CRM systems.
Configuration
Navigate to GUI > Settings > CDR view custom URL.
You can include CDR parameters in the URL using two methods:
- Via Parameters and Custom headers items: Values are appended as query parameters (e.g.,
?paramName=value) - Directly in URL: Use {{paramName}} syntax, which is replaced with the actual value
Display
Configured custom URLs appear as links in the Commands column of the CDR view.
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: This article documents VoIPmonitor GUI settings including sensor configuration (with SSL/TLS parameters for decrypting encrypted SIP traffic), sensor health monitoring via RRD charts (buffer usage and packet drops graphs to diagnose sniffer host overload), troubleshooting server instances that do not appear in the GUI after hardware replacement, CDR custom headers with their limitations, GeoIP data loading, system configuration (basic, database, national, intervals, email, license, GeoIP, advanced), localization, and custom CDR URLs. Advanced settings include Http proxy (for upgrades) for configuring proxy servers behind firewalls, and Pcap deduplication before download which can cause packet count mismatches between GUI SIP History and downloaded PCAP files. Key topics: custom headers store raw SIP header values without regexp extraction or delimiter aggregation; sensor SSL settings (ssl_key, ssl_cert, ssl_ipport) can be configured via GUI wrench icon; sensor health monitoring via RRD charts (Settings > Sensors > chart icon) showing buffer usage and packet drops to diagnose sniffer overload vs network quality issues; sensor troubleshooting for non-deletable local sensors in server/probe deployments; server instance troubleshooting when replacing hardware (server/SBC) and reusing IP address - requires manually creating sensor entry in Settings > Sensors and configuring managerip/managerport in voipmonitor.conf on the new server instance; GUI and sensor upgrades behind proxy servers can be configured via Settings > System Configuration > Advanced > Http proxy (for upgrades) or via curlproxy in voipmonitor.conf for remote sensors; license notification emails can be disabled by removing the email address in Settings > License.
Keywords: GUI settings, sensors, CDR custom headers, header limitations, GeoIP, system configuration, timezone, national prefix, date format, intervals, email settings, license settings, license notification emails, overage notification, advanced settings, localization, custom URL, CSV export, ssl_key, ssl_cert, ssl_ipport, tls decryption, ssl configuration, pcap deduplication, packet count mismatch, missing packets in PCAP, RRD charts, sensor health monitoring, buffer usage, packet drops, sniffer overload, choppy audio, poor call quality, MOS score, sensor capacity limits, server instance troubleshooting, hardware replacement, SBC replacement, reusing IP address, managerip, managerport, server not appearing in GUI, CDR warning about unknown sensor, proxy, http proxy, proxy server, firewall, corporate proxy, GUI upgrade, sensor upgrade, curlproxy, proxy authentication
Key Questions:
- How do I configure sensors in the VoIPmonitor GUI?
- How do I configure SSL/TLS settings for a sensor using the GUI?
- How do I enable TLS decryption for specific trunks through the web interface?
- Where do I find SSL/TLS parameters (ssl_key, ssl_cert, ssl_ipport) in the GUI?
- How do I access sensor RRD charts for health monitoring?
- How do I check if the sniffer host is overloaded using RRD charts?
- What do buffer usage and packet drops graphs indicate in sensor RRD charts?
- How can I tell if poor call quality is caused by the sniffer host vs network issues?
- What does buffer usage at 100% mean for VoIPmonitor sensor performance?
- How do I delete a non-deletable local sensor in a server/probe deployment?
- How do I create and configure CDR custom headers?
- Can I extract part of a SIP header using regexp in custom headers?
- Can I aggregate multiple occurrences of a SIP header?
- What are the limitations of CDR custom headers?
- How do I create alerts based on CDR custom headers?
- How do I load GeoIP data for the map view?
- What system configuration options are available?
- How do I set national prefixes and date/time formats?
- What interval settings control CDR and dashboard filters?
- How do I configure GeoIP services?
- How do I create GUI localizations?
- How do I add custom URLs to the CDR view?
- How do I export CDRs to CSV via crontab scheduler?
- Why does the downloaded PCAP file have fewer packets than shown in the GUI SIP History?
- How do I disable Pcap deduplication before download to include all packets in downloaded PCAP?
- Where do I configure license notification email addresses?
- How do I stop receiving license issue and overage notification emails?
- What should I do if a server/SBC does not appear in the GUI after replacing hardware and reusing the IP address?
- How do I manually create a server instance entry in the GUI?
- What are managerip and managerport configuration options in voipmonitor.conf?
- After replacing a server/SBC, why does data appear in CDRs with warnings but the sensor is not visible in Settings > Sensors?
- How do I configure network connectivity for server instances that connect directly to MySQL database?
- Can I switch from the old server instance architecture to modern Client-Server mode?
- How do I configure HTTP proxy for GUI and sensor upgrades?
- Where is the Http proxy (for upgrades) setting in the GUI?
- How do I configure proxy server in Settings > System Configuration?
- How do I fix GUI upgrade failures behind a corporate proxy or firewall?
- How do I configure curlproxy for remote sensors?
- What is the format for HTTP proxy configuration in VoIPmonitor?