Call Detail Record - CDR
This guide is a comprehensive tour of the main Call Detail Record (CDR) interface in the VoIPmonitor GUI. It explains every section, button, and feature, from searching for calls to analyzing their quality in detail.
What is a CDR?
A Call Detail Record (CDR) is a data record containing information about a single telephone call or communication session. In VoIPmonitor, each CDR captures:
- Call timing (start time, duration, connect time)
- Participant information (caller/called numbers, IP addresses, SIP agents)
- Signaling details (SIP messages, final response codes)
- Quality metrics (MOS scores, packet loss, jitter/delay statistics)
- Media information (codecs, RTP stream data)
The CDR view is the primary interface for searching, filtering, and analyzing these records.
How CDR Fields Are Populated
VoIPmonitor populates CDR fields directly from the SIP INVITE packet. The values recorded are a direct reflection of the data in these SIP headers.
- Calling Number:* Taken from the
Fromheader of the SIP INVITE.
- Called Number:* Taken from the Request-
URIof the SIP INVITE. If the number is not in the URI, theToheader is used instead.
- Caller IP (sipcallerip):* The source IP address of the SIP INVITE packet.
- Called IP (sipcalledip):* The destination IP address of the SIP INVITE packet.
If caller/called numbers or IP addresses appear "inverted" in your CDRs, this typically indicates that the SIP signaling flow in your network is different than expected (for example, the PBX may be initiating a callback). The values are correct as recorded - they simply reflect what is present in the actual SIP headers.
To verify the field mapping, use the SIP History tab in the CDR detail view to inspect the actual SIP INVITE packet and compare the From, To, and URI fields with the CDR columns.
Understanding the Main CDR View
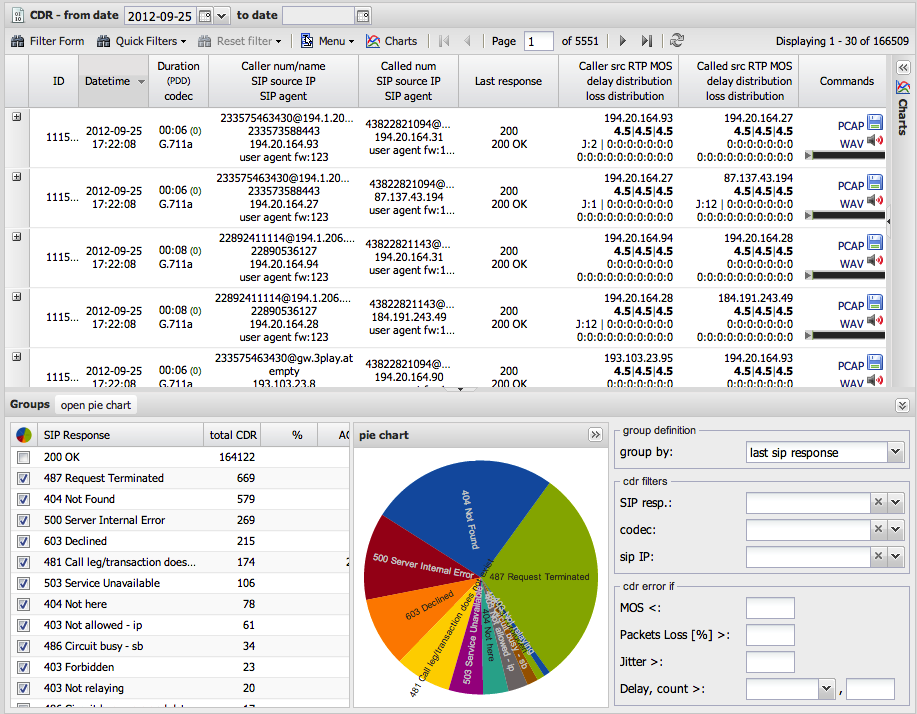
The CDR view is the central hub for exploring your captured call data. It is comprised of three main sections:
- The CDR List: The main table displaying a paginated list of all finished calls.
- The Button Panel: A toolbar for accessing key functions like filtering, charting, and exporting.
- The Dashboard: A set of panels at the bottom that provide aggregated statistics for the currently displayed data.
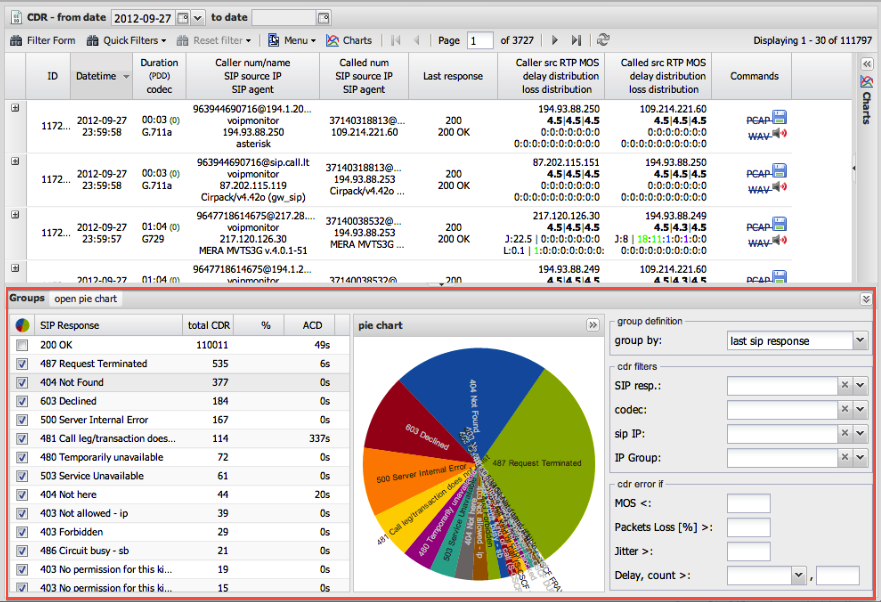
The CDR List
This section details the components of the main call list, from the title bar to the information in each row.
Title Bar & Date Filter
At the very top, the title bar displays the current time range for the calls being shown. You can click on the dates to quickly change the filter.
Timezone Display Setting
In the top right corner of the CDR view, there is a timezone selector that controls how call timestamps are displayed. This setting is user-specific and can shift the displayed time based on your local browser/OS settings, independent of how the data is stored in the database.
Understanding the timezone hierarchy:
- Storage Layer (Sniffer): Controlled by
utcandtimezoneoptions invoipmonitor.conf(see Sniffer Configuration) - GUI Layer (Settings): Controlled by Settings > System Configuration > National > Timezone
- Display Layer (CDR View):** Controlled by the timezone selector in the top right corner (user-specific)
If CDR times appear incorrect, check all three layers in the order listed above.
Note: This quick date filter can be disabled on a per-user basis in user settings.
Button Panel
This toolbar provides access to the most important interactive features.
Understanding the Last SIP Response
The "Last SIP Response" column in the CDR list displays the final SIP response code captured by VoIPmonitor. It is important to understand that this response may not always correspond to the initial INVITE's response.
Why You Might See Different Response Codes
It is possible for a single call to display multiple response codes in different contexts:
200 OK and 5XX/4XX in the Same Call:
- If the Duration' > 0 (call has media): The call WAS successfully connected. The 200 OK indicates successful session establishment. Any later error response (e.g., 503 Service Unavailable) appears in the signaling after the call was connected, typically in a BYE packet's Reason header indicating why the call was terminated.
- If the Duration' = 0 (no media): The call was NOT connected. Multiple signaling responses occurred before session establishment, such as multiple SIP forking legs where one destination answered while another failed.
= Finding the Termination Reason
To understand why a call shows a specific response code (especially 5XX or 4XX codes in the "Last SIP Response" column):
- Locate the call in the CDR list and click the
[+]icon to expand the detail view - Navigate to the SIP History tab
- Find the BYE packet (this is the message that terminates the call)
- Click the magnifying glass icon on the BYE packet row to expand the packet details
- Look for the Reason header in the packet detail tree
The Reason header in the BYE packet contains the SIP response code describing why the call was terminated. For example:
Reason: SIP; cause=503; text="Service Unavailable"
This status may indicate:
- A specific action taken by the called party (e.g., DTMF choice in an IVR system)
- A downstream issue in an SBC or SIP proxy
- Device availability or routing problems
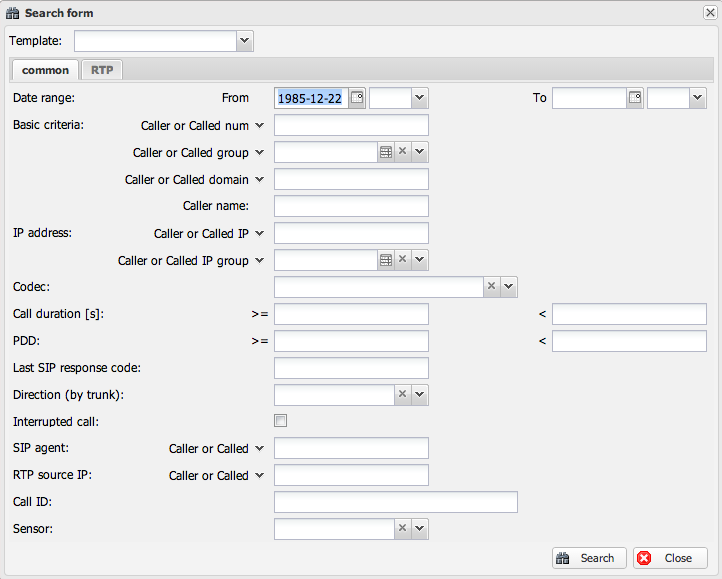
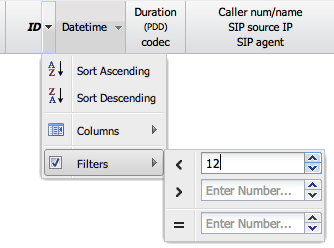
1. Filter Form
This is the most powerful feature for finding specific calls. Clicking this button opens a detailed search form with two main tabs.
Common Tab
This tab contains filters for general call attributes and participant information.
- Participant Filters: Search by
Caller/Called Number,Caller/Called IP, orCaller/Called Domain. You can use the%character as a wildcard (e.g.,222%finds all numbers starting with 222). You can also use commas for multiple values and!for negation (e.g.,222%, !223%).
Regular Expressions for Advanced Number Filtering
The CDR number filters support regular expressions using the R() syntax. This is useful for complex patterns and searching for number ranges.
Basic Regex Examples
Find numbers matching a specific pattern:
R(^500[0-9]{4}$)
Matches exactly 9-digit numbers starting with 500.
Find numbers without digits only (malformed):
!R(^[+]?[0-9]+$)
Negative match to find calls with non-numeric characters in the caller number.
Searching for Number Ranges
To search for a numeric range (e.g., from 171457872 to 171457879), use regex character classes:
R(17145787[2-9]) R(1714578[89])
The space between the two R() patterns acts as OR logic, matching either pattern. This covers all numbers in the range 171457872 through 171457879.
Other Range Examples
Match specific last digits (e.g., 100 through 109):
R(0?1[0]{2}[0-9])
Match numbers ending in specific ranges:
R([0-9]{3}[0-4][0-9])
Match numbers ending in 04X through 09X.
How to Find and Download Audio for Partial Caller + Specific Called Numbers
This workflow allows you to search for calls using a partial match on the calling number (A number) combined with a specific or partial called number (B number), then batch download all the audio files.
- 'Step-by-step procedure:*
- Navigate to the GUI CDR view
- Click the Filter Form button
- In the Common tab, find the Caller/Called Number filter section
- In the caller field, enter the partial number with a
%wildcard:
%123456matches all numbers ending in 123456123%matches all numbers starting with 123
- In the called field, enter the called number (with wildcard if needed):
99999for an exact match999%for a partial match
- Click Apply filter - the view now displays all CDRs matching both criteria
- Click the Menu button
- Select Batch download audio - this downloads audio files (WAV/OGG) for all currently displayed CDRs
- Note: Batch download is limited to 100 records at a time for performance reasons
Example: To download audio for all calls from a specific prefix to a particular destination:
- Caller:
123%(finds all callers starting with 123) - Called:
555(finds exact called number 555)
- Group Filters: Search by pre-defined
Caller/Called GroupsorIP Groups. - IP Address Include Proxy: When filtering by
Caller IPorCalled IP, check the IP Address Include proxy checkbox to include proxy IP addresses from the proxy chain (tracked viacdrproxysetting). This prevents calls with different SIP source and destination IPs from being incorrectly merged in the view. This is particularly useful when:- Calls are routed through multiple SIP proxies where the signaling IP changes at each hop
- You need to see the full proxy chain for a call
- CDRs appear incorrectly merged with different participants but same Call-ID or correlation header
- Disable the checkbox to filter only by the direct SIP source/destination IPs (ignoring proxy chain).
- Call Attribute Filters: Filter by
Call Duration,Codec, orPDD(Post-Dial Delay) ranges. - SIP Filters: Filter by
Last SIP Response Code(e.g.,487, or4%for all 4xx codes),SIP Agent(phone type/firmware),SIP Call-ID, orSIP requests(select a specific SIP method such as INVITE, REFER, BYE, CANCEL, etc.). The SIP requests filter also supports counting occurrences - for example, to find calls with multiple SIP INVITEs (indicating multiple connections or re-INVITEs), set the filter tosip requests: INVITE count >= 3. This allows you to identify calls with complex signaling patterns directly from the CDR list without opening each call. Note: The "SIP requests" dropdown filter requiressave_sip_history = allorsave_sip_history = requeststo be configured in voipmonitor.conf.
Finding re-INVITE Calls
A re-INVITE is an INVITE request sent during an established call to modify the session parameters (e.g., changing IP address, codec, or placing on hold). Re-INVITEs are identified by the presence of a tag in the To header. VoIPmonitor provides two methods to filter for re-INVITE calls:
Method 1: Using SIP Requests Count (recommended for general use)
Use the SIP requests filter in the Common tab to find calls with multiple INVITEs:
- Open Filter Form -> Common tab
- In the
SIP requestsdropdown, select:INVITE - Set count to
>= 3(or>= 2for simpler cases)
This identifies calls where the system recorded multiple INVITE messages, which may indicate re-INVITEs, re-authentication attempts, or call transfers. This method does not require additional configuration beyond save_sip_history.
Method 2: Using Custom Headers toTag (more precise)
For more precise detection of re-INVITEs specifically, you can configure CDR Custom Headers to capture the To header tag and filter based on its presence:
- Configure CDR Custom Headers in Settings -> CDR Custom Headers to capture the
Toheader from INVITE packets. See CDR Custom Headers for configuration details. - Generate new test calls after configuring custom headers (the configuration only applies to new CDRs created after the setting is saved).
- In the CDR view, use the
ToTagfilter with:
%to find calls where the tag is present (indicating a re-INVITE)NULLto find calls where the tag is absent (no re-INVITE)
This method is more specific as it directly checks for the presence of the to-tag in the To header, which is the definitive indicator of a re-INVITE according to the SIP protocol specification. However, it requires custom header configuration and only works for calls captured after the configuration is set.
- Other Filters: You can also filter by the
Sensorthat captured the call or find allInterruptedcalls (those without a proper BYE).
Enabling SIP History
To use the SIP requests filter and to view SIP message details in the CDR detail view, you must enable SIP history capture on the sensor. This feature records SIP signaling details including the number of requests per call (e.g., multiple INVITEs for detecting retransmissions).
Configuration Steps:
- Edit the
voipmonitor.confconfiguration file on the sensor - Add or modify the
save_sip_historyoption:
- Use
save_sip_history = allto capture both SIP requests and responses - Use
save_sip_history = requeststo capture only SIP requests (lighter on database) - Use
save_sip_history = requests,responsesto capture requests and responses explicitly
- Use
- Restart the sensor service to apply the configuration change
After enabling SIP history:
- The
SIP requestsdropdown filter will show the number of SIP messages per call - You can filter for calls with excessive INVITEs (e.g.,
>= 3) to detect SIP retransmissions - The SIP History tab in CDR detail view will display complete SIP message flows
- The SIP requests count will appear in the CDR list column (if enabled in column visibility settings)
Important Notes:
- Only CDRs created after enabling
save_sip_historywill contain SIP request counts - Existing CDRs will not be retroactively populated with SIP history data
- Choose
save_sip_history = requestsoverallin high-traffic deployments to reduce database overhead
Detecting SIP Retransmissions
SIP retransmissions occur when endpoints send duplicate SIP requests (e.g., INVITE, REGISTER) due to network latency or unresponsive servers. Common causes include:
- Network issues causing delayed or lost responses
- Unresponsive SIP servers or PBXs
- High latency paths exceeding SIP transaction timers
VoIPmonitor provides two main ways to detect retransmissions:
1. CDR Filter Method (recommended for identifying affected calls)
- Navigate to the CDR view and click Filter Form
- In the Common tab, locate the
SIP requestsdropdown - Select
INVITE - Set the count operator to
>=and enter3 - This filters for calls with 3 or more INVITEs, which typically indicates multiple INVITE attempts and possible retransmissions
2. SIP History Tab (for detailed analysis)
- Click on a suspicious call to open the CDR detail view
- Navigate to the SIP History tab
- Examine the sequence diagram or message table for repeated INVITEs with identical Call-ID and CSeq values
- Retransmissions appear as vertically stacked identical messages with slightly different timestamps
Note: The SIP REGISTER RRD beta alert type in Alerts can also be used to monitor registration response times, which serves as an indirect indicator of potential REGISTER retransmissions.
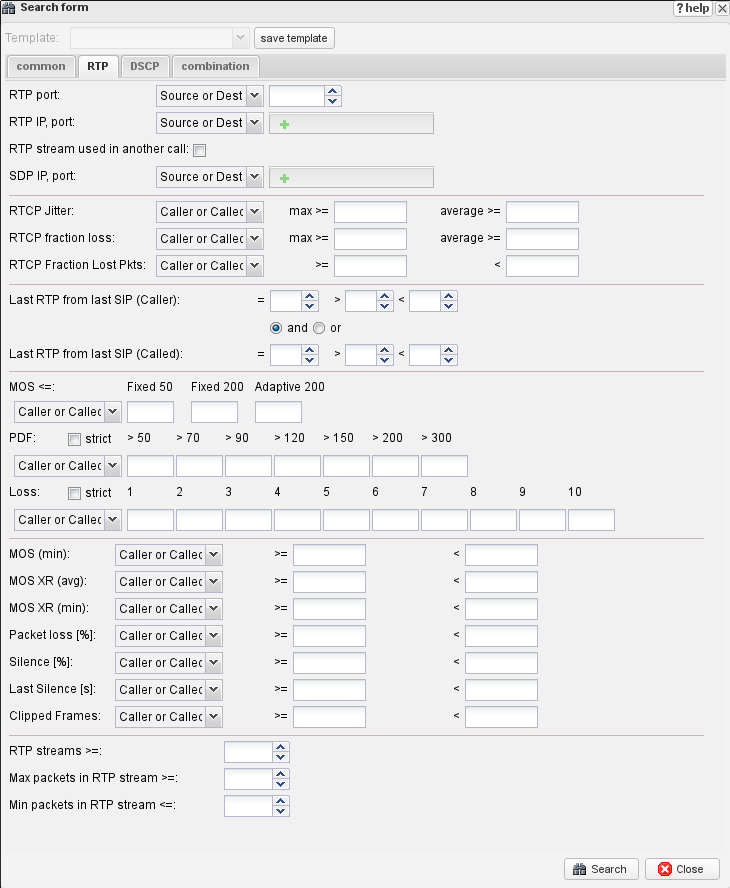
RTP Tab
This tab allows you to find calls based on specific Quality of Service (QoS) metrics. This is essential for troubleshooting audio quality issues.
- RTCP Metrics: Filter by
JitterorFraction Lossvalues reported by the endpoints themselves via RTCP. - MOS: Find all calls with a Mean Opinion Score lower than a specified value.
- PDV (Jitter): Find calls with a specific number of Packet Delay Variation events in different time intervals (e.g., find all calls with at least 10 packets delayed by more than 120ms).
- Loss: Find calls based on patterns of consecutive packet loss.
- Silence & Clipping: If enabled on the sensor, you can find calls with a certain percentage of silence or a specific number of clipped audio frames. See Silence_detection for configuration details.
- Last RTP from Last SIP (caller/called): Find calls where the RTP stream ended before the final SIP packet. This filter is useful for identifying calls with early media stops, one-way audio failures, or calls put on hold where music-on-hold stopped. The filter compares the time when RTP packets stopped flowing to the time of the last SIP signaling packet, returning calls where the media stream terminated prematurely.
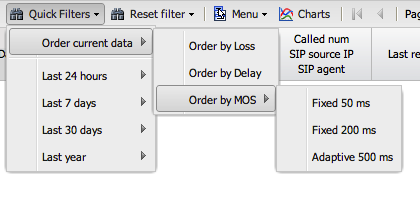
2. Quick Filters
This dropdown provides shortcuts for finding problematic calls (e.g., "Worst Calls by Loss") and gives you access to your saved filter templates.
= Saving and Reusing Filter Templates
You can save frequently-used filter criteria as templates and reapply them later, or combine multiple templates using OR logic.
- 'To save a filter template:*
- Apply your desired filter criteria using the Filter Form.
- Click the Save filter template button (usually shown as a save/disk icon in the filter area).
- Enter a descriptive name for your template (e.g., "Calls dropped within 5 seconds").
- The template will appear in the Quick Filters dropdown menu for future use.
- 'To apply a saved filter template:*
- Click the Quick Filters dropdown.
- Select your saved template from the list.
Combining Multiple Templates (OR Logic)
When you need to find calls matching multiple different criteria at once (for example, all types of call setup failures), use the Combination subtab within the filter form to merge templates using logical OR.
- 'To combine multiple filter templates:*
- Create and save separate templates for each type of filter you need (e.g., one for "Missing BYE", one for "Short calls", one for "5xx responses").
- Open the Filter Form and navigate to the Combination subtab.
- Select all the templates you want to merge.
- The system will return all calls matching ANY of the selected templates (OR logic).
Example use case:' Finding all call setup failures:
- Save template 1: "Interrupted calls" (missing BYE).
- Save template 2: "Short duration (0-5 seconds)" (calls answered then dropped).
- Save template 3: "5xx SIP responses" (server errors).
- Use the Combination subtab to select all three templates.
- Result: One unified CDR view showing all calls with ANY of these failure types.
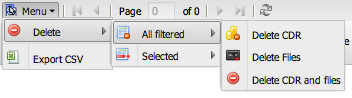
3. Menu
This menu contains administrative actions.
- Delete: Delete selected CDRs and their associated files (PCAPs, audio).
- Export CSV: Export the current view of CDRs to a CSV file.
- Batch download audio: Download audio files for all currently displayed CDRs. This feature allows you to bulk export audio recordings (WAV, OGG, or other formats) based on your current filter criteria. The download is limited to 100 records at a time for performance reasons.
4. Charts
This button opens a window for adding overlay charts to your current CDR view, allowing you to correlate data visually. This feature is covered in detail in the Charts guide.
CDR List Columns
Each column in the CDR list provides key information and can be used for quick sorting.
Customizing Column Visibility
You can show or hide columns in the CDR list based on your preferences. This is useful when:
- You want to reduce visual clutter and focus on specific information
- Certain columns contain data that is causing performance issues
- Your display has limited screen space
To hide or show columns in the CDR view:
- Locate the column header area at the top of the table
- Click on the column visibility icon (typically a column or grid icon)
- Uncheck columns you want to hide, check columns you want to show
- The view will update immediately with your selection
Your column visibility preferences are stored in the GUI configuration (saved in the MySQL custom_config table) and persist across sessions.
Column Reference
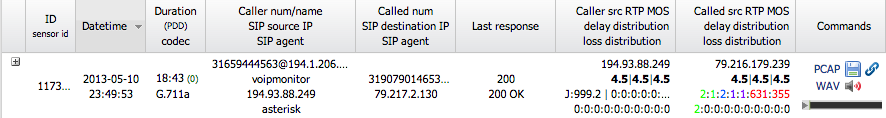
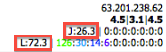
A single row represents a single call.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | The unique identifier for the call record (primary key in the database) |
| Sensor ID | The name of the sensor that captured the call (see Sensors configuration) |
| Datetime | The start time of the call (from first INVITE) |
| Duration (PDD) / Codec | Total call duration, Post-Dial Delay, and the audio codec used |
| Caller/Called Info | Number, Name, SIP IP, and SIP Agent. The red flag |
| Last Response | The final SIP response code and text for the call |
| RTP IP Addresses | Source IP addresses for the caller and callee RTP streams |
Quality Metric Columns
The quality columns provide at-a-glance indicators of call quality:
- MOS Column
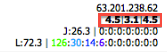 : Shows three parametric MOS scores based on different jitter buffer simulations:
: Shows three parametric MOS scores based on different jitter buffer simulations:
- F1: Fixed 50ms jitter buffer
- F2: Fixed 200ms jitter buffer
- Adapt: Adaptive jitter buffer (up to 500ms)
- Delay Column
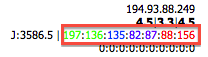 : Color-coded distribution of packet delay variation (jitter) events. See Jitter Analysis for interpretation.
: Color-coded distribution of packet delay variation (jitter) events. See Jitter Analysis for interpretation.
- Loss Column
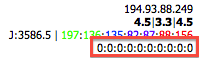 : Color-coded distribution of consecutive packet loss events. Red indicates burst losses which are more harmful to quality.
: Color-coded distribution of consecutive packet loss events. Red indicates burst losses which are more harmful to quality.
- PRICE Column: Shows billing costs calculated by the billing system. This column is hidden by default and must be enabled manually. To enable the PRICE column:
- Click the dropdown menu on the first column (the column header with the ID or the column selection icon)
- Select PRICE from the list of available columns
- The PRICE column will now display Customer (C:) and Operator (O:) prices for each call
Note: Costs only appear if billing is configured (see Billing Configuration) and "Enable by addresses" or "Enable by numbers" is checked in the billing settings. The "Default customer billing" checkbox ensures customer prices are applied to all source IPs by default, which may be useful for reporting purposes.
Understanding Sniffer vs RTCP Packet Loss
VoIPmonitor provides two different packet loss metrics measured from different network locations:
Interpretation Guide:
| Scenario | Likely Cause |
|---|---|
| RTCP loss > Sniffer loss | Network issue after the sniffer (Wi-Fi, last-mile, endpoint network) |
| Sniffer loss > RTCP loss | Monitoring point dropping packets (CPU overload, interface saturation) or RTCP reports not captured |
| High RTCP loss, good MOS | Packet Loss Concealment (PLC) effectively hiding scattered losses |
Troubleshooting tips:
- Trust RTCP loss for user experience issues - it reflects what the device actually received
- Use sniffer loss for network health monitoring in the segment you control
- When RTCP loss is higher, investigate the network path between sniffer and endpoint
Commands Column
- Download links for PCAP and WAV files
- Embedded audio player to listen directly in the browser
The CDR Detail View
Clicking the [+] icon at the beginning of any CDR row expands it to show the detailed analysis view with multiple tabs.
Summary Tab
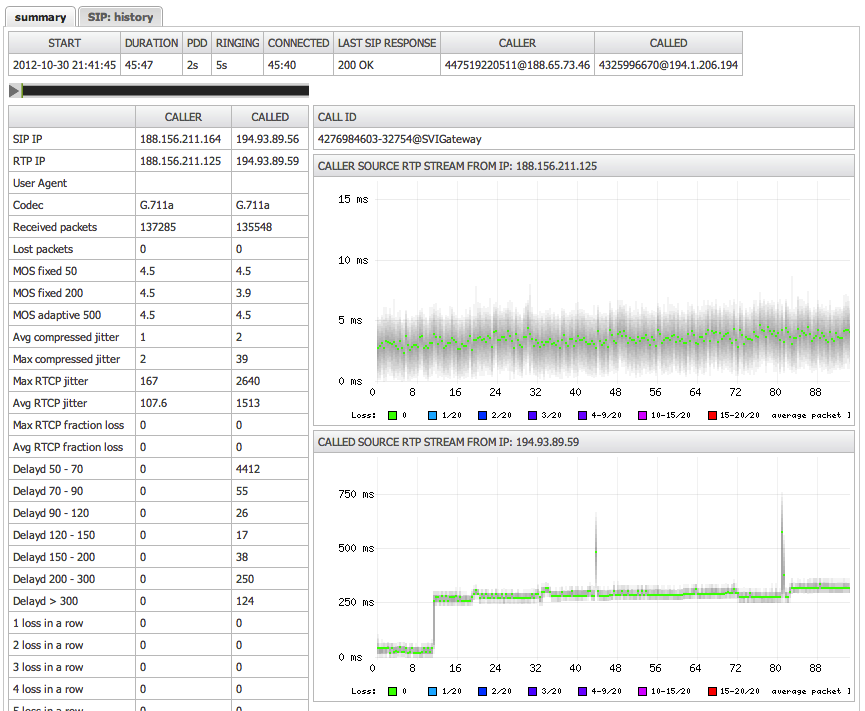
This tab provides a detailed breakdown of call information, RTP statistics, and a full chronological log of all SIP messages for the call.
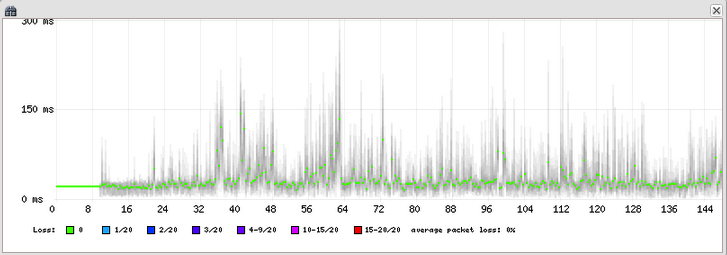
The Call Quality Graph
The most prominent feature is the detailed quality graph, which plots packet delay and loss over the duration of the call.
- Each vertical line represents a group of packets
- The colored dot represents the median delay (jitter)
- Packet loss is shown as red lines at the top of the graph
- Clock Drift: A graph that steadily climbs or descends
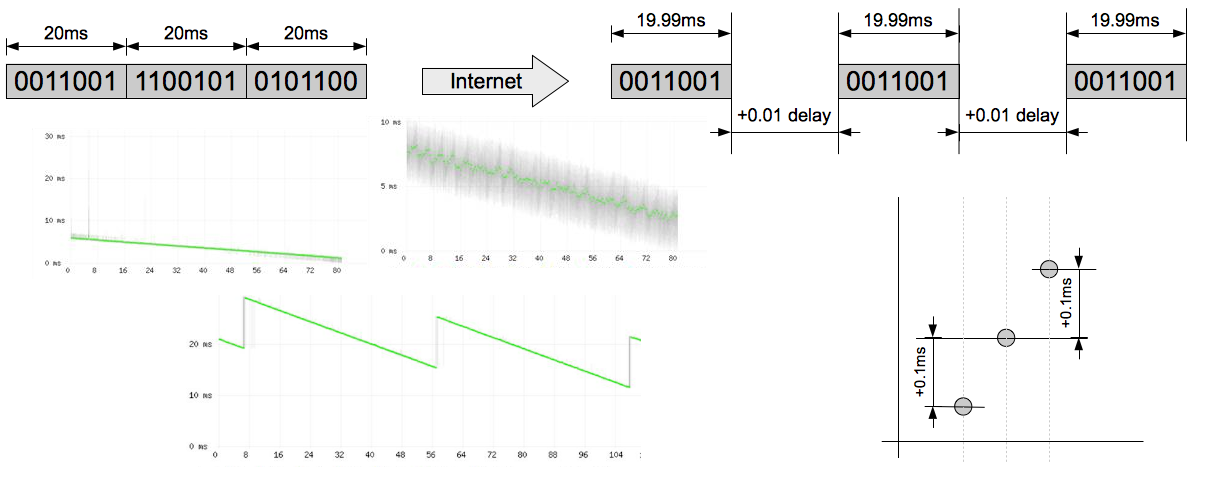 indicates a clock drift issue between the sending device and the sensor, not necessarily a network problem
indicates a clock drift issue between the sending device and the sensor, not necessarily a network problem
How Delay Causes Packet Loss (Jitter Buffer Behavior)
The graph plots delay (median delay/jitter), not constant one-way latency. This distinction is important because large delays directly cause packet loss in real-world calls.
Here is what happens when you see increasing delay on the graph:
1. RTP packets normally arrive every 20ms (for standard codecs) 2. When the delay increases (the dot moves higher), packets are arriving later than expected 3. The receiving device uses a jitter buffer to smooth out these variations 4. If a packet arrives too late (exceeding the jitter buffer capacity, typically 50-200ms depending on the device), it gets skipped during audio playback 5. VoIPmonitor detects this as missing sequence numbers and reports it as packet loss
This is why you will often see patterns where: high delay regions on the graph correlate with red packet loss lines appearing nearby. The delay itself is not a quality issue per se, but when it becomes too large, packets get dropped because they cannot be played in time.
For detailed information on how jitter buffers work and how delay patterns affect MOS scores, see Jitter Buffer Simulation.
Received Packets (Caller / Called)
The "received packets" field in the CDR grid shows how many RTP packets the VoIPmonitor sniffer received FROM that endpoint, not how many packets the endpoint itself received.
| Field | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Caller → Received Packets | Number of RTP packets VoIPmonitor received from the caller (A-leg) |
| Called → Received Packets | Number of RTP packets VoIPmonitor received from the called party (B-leg) |
One-Way Stream Example: If you have a unidirectional RTP stream (caller → called only):
- Caller column shows: 73 packets (VoIPmonitor received 73 packets from the caller's stream)
- Called column shows: empty (VoIPmonitor received no packets from the called party)
This indicates that VoIPmonitor sniffed packets sent by the caller, but did not capture any return stream from the called party.
Bidirectional Stream: Both columns will have values when VoIPmonitor receives RTP packets from both endpoints.
DTMF Section
When DTMF capture is enabled on the sensor, the Summary tab displays a dedicated **DTMF section** that shows all DTMF digits pressed during the call.
To enable DTMF capture, configure voipmonitor.conf:
- For SIP INFO and RTP RFC 2833 methods, set:
dtmf2db = yes - For in-band DTMF (G.711 codec only, CPU intensive), set:
inbanddtmf = yes
Once enabled, the DTMF digits are stored in the database and appear in this section, along with being viewable in the SIP History tab (for INFO messages) or in dedicated DTMF charts/tables for RFC2833 events. See the FAQ for more DTMF configuration details.
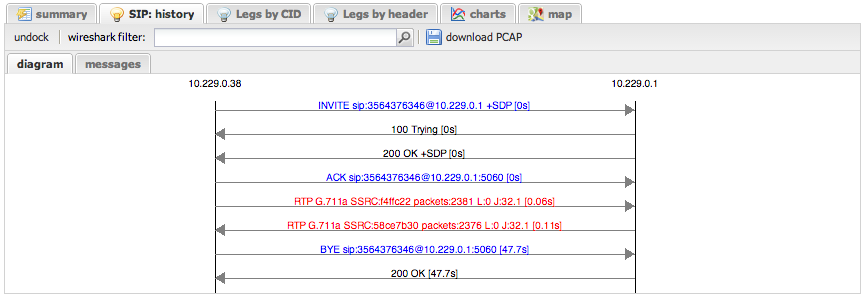
SIP History Tab
This tab provides a powerful, Wireshark-like view of the call's signaling.
- Sequence Diagram: A visual representation of the SIP message flow between endpoints
- Message Table: A text-based list of all SIP messages and RTP streams
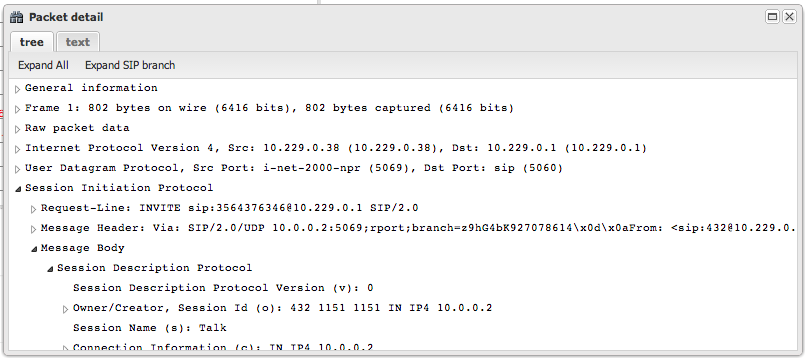
- Packet Detail: Clicking on any message opens a window with a fully decoded tree view of the packet, similar to Wireshark
Legs by CID / Legs by Header Tabs
These tabs are used to find related call legs in complex call scenarios. For detailed information about call correlation, see Merging_or_correlating_multiple_call_legs.
- Legs by CID: Finds other calls that share the same numeric part of the
Fromheader tag within a few seconds of the original call. This is useful for finding the other legs of a call that was routed through a PBX.
- Legs by Header: A more powerful method that correlates calls based on a shared identifier in a custom SIP header (configured by
match_headerinvoipmonitor.conf). This is essential for tracing a single call across multiple proxies or SBCs where the Call-ID changes at each hop.
Charts Tab
This tab displays a set of predefined and custom charts applied specifically to the context of the selected call (e.g., showing trends for the caller number). This allows for quick historical analysis without leaving the CDR view.
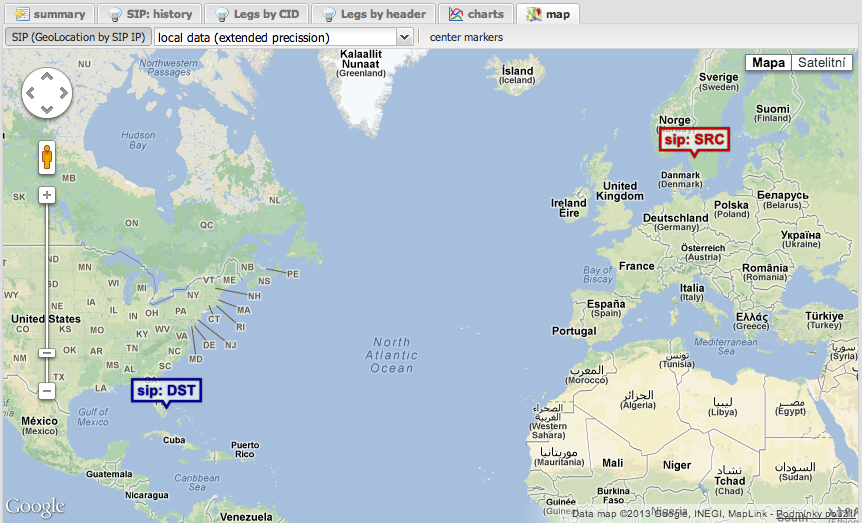
Map Tab
This tab attempts to geolocate the source and destination SIP IP addresses on a world map using a GeoIP service.
The Dashboard Panels
The panels at the bottom of the screen provide aggregated views of the data currently displayed in the CDR list.
- Group By: You can group the data by
Last SIP Response,Codec,SIP IP, or predefinedIP Groups - Charts: The middle section displays a pie chart of the grouped data
- Filters: Clicking on any item in the group grid (e.g., clicking on the "200 OK" response) will instantly apply it as a filter to the main CDR list above
Trend Analysis for Capacity Planning
The grouping tab supports trend analysis that helps with capacity planning. When you group by source or destination IP (SIP IP) or predefined IP Groups, you can:
- View Trends by Source/Destination IP: Navigate to the Grouping tab at the bottom of the CDR view and select "SIP IP" as the grouping option. This allows you to visualize call volume trends for specific source or destination IP addresses over time.
- Capacity Planning Use Case: By analyzing trends grouped by IP address, you can identify high-traffic sources or destinations that may require scaling. This is particularly useful for:
- Planning additional bandwidth for SIP trunks
- Identifying growth patterns for customer traffic
- Forecasting hardware needs based on IP address trends
- CDR Trend Alerts: In addition to viewing trend data interactively, you can configure alerts to trigger automatically based on CDR trends. See Alerts for information on setting up trend-based alerts for proactive capacity planning.
Limitations & Known Issues =
Media Encryption (SRTP, DTLS, ZRTP) Filtering
VoIPmonitor captures and can decrypt SRTP and DTLS (see TLS/SRTP Decryption Guide for decryption configuration), but there is no filter for media encryption protocols (SRTP, DTLS, ZRTP) in the CDR view.
| Encryption Type | Support | How to Verify |
|---|---|---|
| Supported (can decrypt if configured) | Manual verification via SIP History tab | ||
| NOT supported | Cannot monitor ZRTP-encrypted calls |
How to Manually Verify SRTP/DTLS Usage:
If you need to verify whether a specific call used SRTP or DTLS encryption, you must inspect the SDP content in the SIP signaling:
- Click on a CDR row to expand the detail view
- Navigate to the SIP History tab
- Click on the SIP INVITE packet
- Expand the SDP section and look for:
a=cryptolines - indicate SRTP encryptiona=fingerprintanda=setupattributes - indicate DTLS-SRTP negotiation
⚠️ Warning: ZRTP is NOT Supported: VoIPmonitor does not currently support monitoring or decrypting ZRTP-encrypted calls. Calls using ZRTP will appear as encrypted/unclear media stream in the GUI, and their details cannot be inspected.
Related Documentation
- Database_structure - Technical reference for CDR database columns
- Comprehensive_Guide_to_VoIP_Voice_Quality - In-depth guide to MOS, jitter, and quality metrics
- Merging_or_correlating_multiple_call_legs - How to correlate call legs across systems
- Silence_detection - Audio analysis features (silence/clipping detection)
- Reports - Generating reports from CDR data
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: The CDR (Call Detail Record) View is the primary interface in VoIPmonitor GUI for analyzing captured calls. It consists of three main sections: the CDR List (paginated call records), Button Panel (filtering and export tools), and Dashboard (aggregated statistics). The Filter Form provides powerful search capabilities through two tabs: Common (participant info, duration, SIP filters) and RTP (quality metrics like MOS, jitter, packet loss). In the Common tab, you can filter by Caller/Called Number using the dropdown menu, and use the % wildcard for partial matching (e.g., "123%" matches all numbers ending in 123, or "%456" matches all numbers starting with 456). You can filter on both caller and called fields simultaneously. To download audio files for calls matching specific number patterns: navigate to GUI CDR view, click Filter Form button, in the Common tab enter partial caller with wildcard (%123456 for suffix, 123% for prefix) and called number, apply filter, then click Menu button and select Batch download audio - this downloads all audio files for currently displayed CDRs, limited to 100 records at a time. Filter templates can be saved and reused, and multiple templates can be combined using OR logic via the Combination subtab to find calls matching different criteria simultaneously (useful for finding all types of call setup failures). The Menu button provides actions including Delete, Export CSV, and Batch download audio - the latter allows bulk download of audio files (WAV, OGG) for all currently displayed CDRs, limited to 100 records at a time. Each CDR row displays call timing, participant information, and quality metrics including three MOS scores (F1, F2, Adaptive) based on different jitter buffer simulations. The RTCP column shows endpoint-reported metrics; when RTCP loss is higher than sniffer loss, it indicates network issues after the monitoring point (Wi-Fi, last-mile). The Dashboard panels at the bottom support trend analysis for capacity planning - you can group by SIP IP and view trends by source/destination IP addresses to identify traffic growth patterns and plan bandwidth or hardware scaling. The Detail View (accessed by expanding a row) includes the Summary tab with quality graphs and a DTMF section (when enabled), SIP History tab with Wireshark-like packet analysis, and Legs by CID/Header tabs for correlating related call segments across systems. To view DTMF digits pressed during a call, enable DTMF capture with dtmf2db and/or inbanddtmf in voipmonitor.conf, then DTMF digits appear in the Summary tab's dedicated DTMF section and in the SIP History tab. For SIP retransmissions detection: first enable save_sip_history in voipmonitor.conf (save_sip_history = requests,responses) and restart the sensor service, then use the CDR Filter Form's SIP requests dropdown to filter for INVITE messages with count >= 3 to identify calls with likely retransmissions, or use the SIP History tab to visually inspect repeated SIP messages with identical Call-ID values. The RTP tab in the Filter Form includes specialized filters for finding calls with specific timing issues. The "Last RTP from Last SIP (caller/called)" filter finds calls where the RTP stream ended before the final SIP packet - useful for identifying calls with early media stops, one-way audio failures, or calls put on hold where music-on-hold stopped. This filter compares when RTP packets stopped flowing to the time of the last SIP signaling packet, returning calls where the media stream terminated prematurely. To access this filter: navigate to GUI > CDR > Filter form, open the 'RTP' subtab, and use the 'Last RTP from Last SIP (caller/called)' filter field. IMPORTANT LIMITATION: There is NO filter for media encryption protocols (SRTP, DTLS, ZRTP) in the CDR view. VoIPmonitor cannot monitor ZRTP-encrypted calls (ZRTP is NOT supported). To manually verify SRTP/DTLS usage, inspect the SDP content in the SIP History tab: click CDR row to expand, open SIP History tab, click SIP INVITE, expand SDP section, and look for a=crypto lines (SRTP) or a=fingerprint and a=setup attributes (DTLS-SRTP). See the TLS documentation for SRTP decryption configuration. To understand why a call shows a specific response code in the "Last SIP Response" column (e.g., 503 Service Unavailable), expand the CDR detail view, navigate to SIP History tab, find the BYE packet, click the magnifying glass icon to expand packet details, and look for the Reason header which contains the SIP response code describing why the call was terminated (e.g., Reason: SIP; cause=503; text="Service Unavailable"). A call can show both 200 OK and a 5XX/4XX code: if Duration > 0 the call was connected (200 OK for session establishment) and the error appears in BYE's Reason header indicating termination reason; if Duration = 0 the call was never connected and multiple responses occurred during signaling (e.g., SIP forking).
Keywords: CDR, call detail record, GUI, filter, search, MOS, jitter, PDV, packet loss, quality metrics, SIP history, sequence diagram, call legs, correlation, dashboard, group by, RTCP, sniffer loss, endpoint loss, trend analysis, capacity planning, source IP, destination IP, SIP IP, traffic trends, SIP requests filter, INVITE count, multiple connections, re-INVITE, toTag, custom headers, CDR custom headers, to header filter, tag presence, filter template, save filter, Combination subtab, OR logic, combine filters, quick filters, batch download audio, WAV, OGG, partial match, wildcard, caller dropdown, called dropdown, export audio, DTMF, dtmf2db, inbanddtmf, DTMF digits, DTMF section, save_sip_history, SIP history capture, enable SIP history, voipmonitor.conf configuration, sensor restart, SIP retransmissions, multiple INVITEs detection, retransmission detection, SIP request count, network latency REGISTER RRD beta alert, download audio, audio files, partial number, caller wildcard, called wildcard, A number, B number, calling number, partial caller, specific called, exact called, calling number match, download multiple audio, RTP filter, RTP tab, Last RTP from Last SIP, RTP timing, RTP end before SIP, early media stops, one-way audio, music on hold, media stream termination, premature media stop, SRTP, DTLS, ZRTP, encryption, encrypt, media encryption, no filter, not supported, manual verification, SIP History, SDP, a=crypto, a=fingerprint, a=setup, encrypted calls, last SIP response, BYE packet, Reason header, termination reason, 503 Service Unavailable, call duration, duration zero, duration non-zero, SIP forking, magnifying glass icon, packet details, 200 OK, 5XX response, 4XX response, call connected, call not connected, SBC, downstream issue
Key Questions:
- How do I use the CDR view to find specific calls?
- How can I view trends by source or destination IP in the CDR view?
- How can I filter calls by quality metrics (MOS, jitter, loss)?
- What do the MOS F1, F2, and Adaptive scores mean?
- How do I view the SIP message flow for a call?
- What is the difference between Legs by CID and Legs by Header?
- How do I correlate related call legs across multiple systems?
- What does the quality graph show and what indicates clock drift?
- How do I use the dashboard panels to analyze call statistics?
- What is the difference between sniffer loss and RTCP loss?
- Why might RTCP loss be higher than sniffer loss?
- How do I identify calls with multiple SIP INVITEs or multiple connections?
- How can I use the SIP requests filter to count and filter by the number of SIP messages?
- How do I find calls containing re-INVITEs using CDR Custom Headers and toTag filtering?
- How do I save a filter template in the CDR view?
- How do I use the Combination subtab to combine multiple filter templates with OR logic?
- How can I find all types of call setup failures at once using filter templates?
- How do I use the Batch download audio feature in the Menu?
- How do I filter by caller or called number with partial matching using wildcards?
- How can I download audio files for multiple calls at once from the CDR view?
- How do I download audio files based on partial caller and specific called numbers?
- How do I find and download audio for calls with partial calling number (A number) and known called number (B number)?
- How do I enable SIP history capture in voipmonitor.conf?
- What are the save_sip_history configuration options for SIP history?
- Do I need to restart the sensor after configuring save_sip_history?
- How can I detect SIP retransmissions using the CDR view?
- What information does the SIP requests filter require to be enabled?
- How do I find calls with multiple SIP INVITEs to detect retransmissions?
- What is the difference between save_sip_history = all and save_sip_history = requests?
- Where can I view DTMF digits pressed during a call?
- How do I enable DTMF capture and view DTMF digits in the CDR detail?
- What do I need to configure to see DTMF information in the Summary tab and SIP History tab?
- How do I enable DTMF capture and view DTMF digits in the CDR detail?
- What do I need to configure to see DTMF information in the Summary tab and SIP History tab?
- How do I filter calls by media encryption (SRTP, DTLS, ZRTP)?
- Is there a CDR filter for encrypted calls or encryption protocols?
- How can I verify if a call used SRTP or DTLS encryption?
- Does VoIPmonitor support ZRTP encryption monitoring?
- How do I check for SRTP DTLS encryption in the SIP History tab
- Can I filter CDRs by encryption type like SRTP DTLS or ZRTP?
- How do I manually verify encryption for a specific call in the CDR view?
- What SDP attributes indicate SRTP or DTLS encryption?
- Where can I find a=crypto or a=fingerprint attributes in the CDR view?
- How do I find calls where the RTP stream ended before the final SIP packet?
- What is the Last RTP from Last SIP filter for?
- How do I use the CDR RTP tab to find calls with early media stops?
- How can I identify calls with one-way audio failures in the CDR view?
- Where is the Last RTP from Last SIP (caller/called) filter located?
- How do I find calls where the media stream terminated prematurely?
- Why does my call show both 200 OK and 503 Service Unavailable?
- How do I find the termination reason in the CDR view?
- What does the Last SIP Response column mean in the CDR list?
- How do I inspect the BYE packet to find why a call terminated?
- How do I find the Reason header in a BYE packet?
- Where can I view the termination reason for a call in the GUI?
- How do I use the magnifying glass icon to view SIP packet details?
- What does it mean when a call has Duration > 0 with a 503 response?
- What does it mean when a call has Duration = 0 with 200 OK and 503?
- How can I tell if a call was connected or not based on duration and response codes?
- Where do I find the BYE packet in the CDR view?
- What causes a 503 Service Unavailable in the BYE packet?
- How do I interpret multiple response codes for a single call?