Register
The SIP Register section shows three tables - Active registered SIP users, Failed registrations and State changes in SIP registrations. Those tables are filled once you enable sip-register = yes in /etc/voipmonitor.conf.
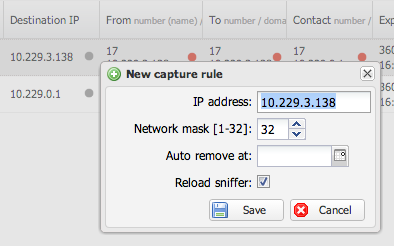
By default PCAP files are not saved for SIP register messages (it can easily overload file system). If you need to record SIP messages you can control this in capture rules main section and here in all three sections there are gray/red small circles which indicates if SIP messages are being recorded to pcap file so it can be retrieved by clicking on PCAP link. Clicking on the circle enables / disables recording. In the dialog window you can adjust values and set auto remove for the rule at specific date. Note: If you need to record all register packets by the sniffer instance without need to create capture rules in a GUI use sip-register-save-all=yes in its config (/etc/voipmonitor.conf)
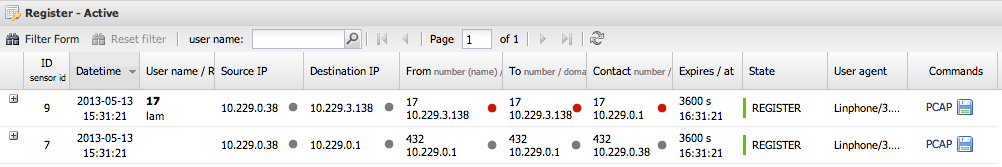
Active table
The active table shows current registered users with this columns:
- ID/sensor id shows internal unique ID and if enabled sensor id
- datetime is time creation
- User name / realm shows username and realm from REGISTER message
- Source IP / Destination IP
- From / To / Contact are values from SIP headers
- Expires at shows date when the registration expires
- User agent
- Commands - download PCAP
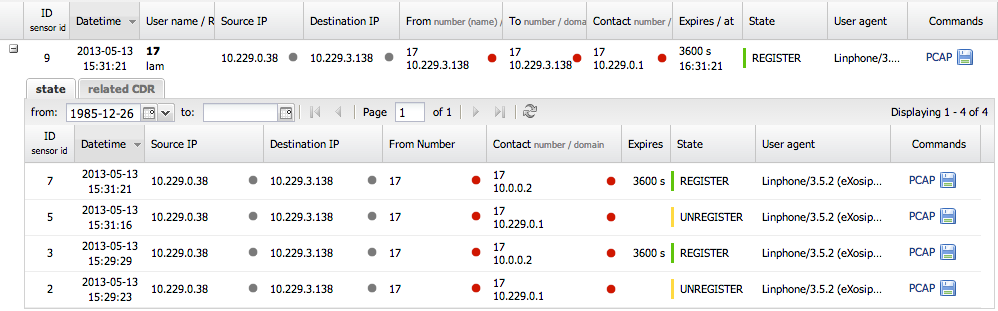
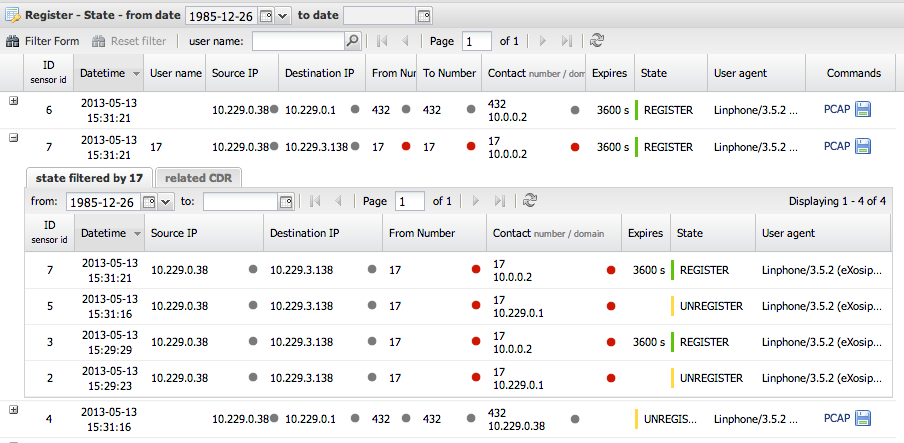
On the picture below you can see a detail area where a sub-grid with state changes and failed registrations from the user name is located. This holds quick filters for a particular active user where you can quickly see his history. Once the SIP registration is expired the history is no longer in the Active table . Each expired registration is stored in the State table.
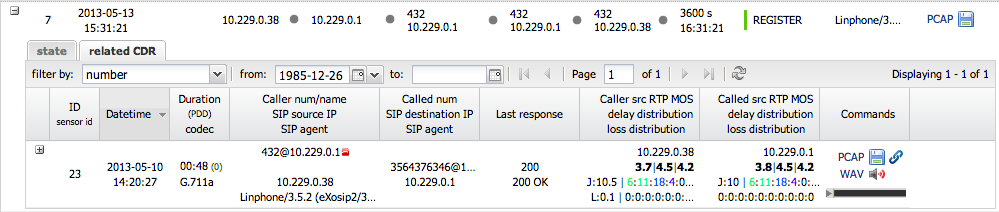
On the picture below you can see a detail area where a sub-grid with related CDR from the user name is located.
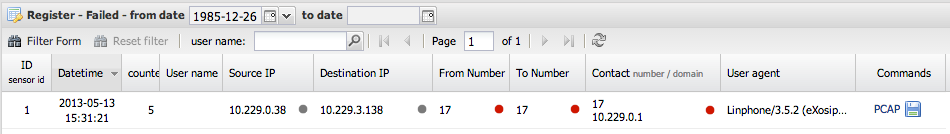
Failed table
The failed table shows failed SIP registrations. If some device fails to register continuously the counter column increases instead of creating a new row. If there is a one-hour gap between two failed registrations from the same user a new row will be created.
State table
The state table retains registration history where REGISTER, UNREGISTER and EXPIRE are saved. In each state row you can click on detail [+] to show all related SIP register messages to the selected user. If device registers in regular intervals it will not save state change in the state table (not true now, see bellow) but keeps the last registration status until the re-registration stops - then UNREGISTER will be the last register state change. If the device do not resend registration in time (register expires + 5 second) the last state will be EXPIRE (with red flag).
The same state is periodically saved due to e.g. graphing, etc. The default is 600 seconds. It can be changed by sip-register-state-timeout option in the sensor config.
Configuration Location in Distributed Architecture
In distributed/client-server deployments, the location where you must enable sip-register = yes depends on your packetbuffer_sender configuration:
| Mode | Configuration Location | Processing Location |
|---|---|---|
| Central server | Central server processes raw packets from remote sensors | ||
| Remote sensor | Each sensor processes packets locally before sending CDRs to central server |
To determine where to configure sip-register:
- 1. Check the
packetbuffer_sendersetting on your remote sensors
grep packetbuffer_sender /etc/voipmonitor.conf
- 2. If
packetbuffer_sender = yes
- Configure
sip-register = yeson the **central server's**/etc/voipmonitor.conf - Restart the voipmonitor service on the central server
- 3. If
packetbuffer_sender = no(or not set)
- Configure
sip-register = yeson the **remote sensor's**/etc/voipmonitor.conf - Restart the voipmonitor service on the remote sensor(s)
For detailed information on distributed architectures and configuration locations, see Sniffer_distributed_architecture.
How the Active tab retrieves data
The Active table in the GUI displays registration data in two different ways, depending on whether the sip-register feature is enabled:
- When sip-register is disabled (default):* The GUI retrieves active registration data directly from the running sniffer processes in real-time. The sniffer maintains an in-memory list of currently registered SIP devices and provides this information to the GUI. In this configuration, the database tables (register, register_state, register_failed) are not created or used. The Active tab will still function correctly and show live registration data.
- When sip-register = yes:* Registration data is stored in database tables (register, register_state, register_failed) for persistent storage and historical reporting. The GUI can then query these tables to display both current and historical registration information.
Displaying Multiple Registrations for the Same Account Independently
By default, multiple registrations for the same SIP account (same username) from different IP addresses or ports may be displayed as a single aggregated record in the GUI Active table. To view all registrations for the same account separately (differentiated by their source and destination IP addresses and ports), enable comparison options in the sniffer configuration file.
Add these lines to /etc/voipmonitor.conf (the configuration that processes sip-register=yes):
# Enable independent display of multiple registrations for the same account sip-register-compare-sipcallerip = yes sip-register-compare-sipcallerport = yes sip-register-compare-sipcalledip = yes sip-register-compare-sipcalledport = yes # Optional: Track registration state changes separately by From domain # Useful when the same SIP account registers from different domains sip-register-state-compare-from_domain = yes
These settings instruct the system to create separate registration entries when the source IP (sipcallerip), source port (sipcallerport), destination IP (sipcalledip), destination port (sipcalledport), or From domain differ. This allows you to see each registration instance independently rather than having them merged into a single record. The sip-register-state-compare-from_domain option is particularly useful for accurate alerting when multiple registrations from the same account should be tracked separately based on their originating domain.
After modifying the configuration, reload or restart the voipmonitor service for changes to take effect.
In distributed architectures, apply these settings to the same location where sip-register = yes is configured (central server for packetbuffer_sender=yes, or remote sensor for packetbuffer_sender=no).
Error: Table 'voipmonitor.register' doesn't exist
If you see the error message "Table 'voipmonitor.register' doesn't exist" when viewing the Active tab, this is expected and correct behavior when the sip-register feature is disabled.
The error message typically appears if the GUI attempts to query the database table for historical information while the feature is disabled. However, the Active tab will still display live registration data retrieved directly from the sniffer processes.
No action is required to fix this error.' The system is functioning as intended. The error simply indicates that persistent database storage is not enabled for registration data.
If you want to enable persistent storage of registration history, add sip-register = yes to /etc/voipmonitor.conf and restart the sniffer. This will create the database tables and eliminate the error message, but it is optional for basic registration monitoring.
Troubleshooting: Registration Data Missing Despite Traffic Being Present
If SIP registration information is missing from the GUI even though traffic is confirmed present on your network mirror port, the issue is likely with packet capture rather than the sip-register configuration. Follow these troubleshooting steps:
- 1. Verify packets are reaching the sensor host
Run a packet capture directly on the sensor to verify REGISTER packets are arriving at the interface. Use tcpdump or tshark on the correct interface:
# Check for REGISTER packets on the sensor interface
tcpdump -i napa0 -s 0 -c 10 "port 5060 and udp"
# Or use tshark for more detailed analysis
tshark -i napa0 -Y "sip.Method == REGISTER" -c 10
If no packets appear, the problem is with your network mirroring configuration (SPAN/TAP). See Sniffer_troubleshooting for detailed packet capture troubleshooting.
- 2. Check for packet drops in the GUI
Navigate to Settings → Sensors in the VoIPmonitor GUI. Expand the sensor details and check the # packet drops counter.
| Packet Drops Value | Meaning | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | No drop issues |
| Non-zero value | Sensor is dropping packets | See Sniffer Troubleshooting: Sensor Statistics |
- 3. If using Napatech hardware
Standard capture tools may show no packets if Napatech interfaces are in a DOWN state. This is a common issue with Napatech cards.
Check interface status:
ip link show napa0
If the interface shows DOWN instead of UP, the solution is to use a custom libpcap library provided by Napatech. See Napatech Troubleshooting for detailed steps to:
- Check if Napatech drivers are loaded
- Verify voipmonitor is linked against Napatech libpcap
- Rebuild the sniffer with the correct library
The key command to verify:
# Check which libpcap voipmonitor is using
ldd /usr/local/sbin/voipmonitor | grep pcap
# Should show: /opt/napatech3/lib/libpcap.so.1
# NOT: /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpcap.so.1
- 4. Additional troubleshooting resources
- Sniffer_troubleshooting - Comprehensive guide for diagnosing packet capture issues
- Network traffic verification with tshark
- Sniffer_troubleshooting#Check_the_VoIPmonitor_Configuration - Verify interface, sipport, and filter settings
Slow Queries on register_state Table
If queries on the register_state table are extremely slow or time out when filtering by text fields (Username, Domain, Number), especially for older data, this indicates missing indexes on frequently queried columns.
Problem Description
The register_state table stores SIP registration history (REGISTER, UNREGISTER, EXPIRE events). Because SIP devices re-register frequently (typically every 30-60 seconds), this table accumulates rows very quickly. Queries filtering by text fields without proper indexes require full table scans, which are extremely slow on large tables.
Common Symptoms
- Queries with filters on Username, Domain, or Number time out
- Searches for specific registration events take 30+ seconds or indefinite
- GUI Register State tab is unresponsive when applying filters
- MySQL shows high CPU usage from register_state queries
Solution: Create Missing Indexes
The root cause is almost always missing indexes on columns used in WHERE clauses. Create indexes manually on the most frequently queried columns.
First, verify which indexes already exist:
-- Show current indexes on register_state
SHOW INDEX FROM register_state;
Look for indexes on:
digestusernamedigest_from_numberdigest_to_numberdigest_to_domaindigest_realm
If these indexes are missing, create them:
-- Create index on username (most common query)
CREATE INDEX digestusername ON register_state (digestusername);
-- Create indexes on other frequently queried columns
CREATE INDEX digest_from_number ON register_state (digest_from_number);
CREATE INDEX digest_to_number ON register_state (digest_to_number);
CREATE INDEX digest_to_domain ON register_state (digest_to_domain);
CREATE INDEX digest_realm ON register_state (digest_realm);
⚠️ Warning:
CREATE INDEX operations on large tables can be very slow and may block write operations to the table. Schedule index creation during a maintenance window or low-traffic periods.
Additional Performance Optimization
If performance is still insufficient after adding indexes:
1. Increase innodb_buffer_pool_size in MySQL configuration (see Scaling Guide)
2. Configure cleandatabaseregister = 7 (or 30) in /etc/voipmonitor.conf to limit data retention (see Data_Cleaning)
ℹ️ Note:
Calculating Required innodb_buffer_pool_size for High-Volume REGISTER Data
For systems with high REGISTER volume (e.g., 30 million records per day), determining the maximum history you can store without performance degradation requires calculating the correct innodb_buffer_pool_size.
= Understanding the Limit
The "maximum" history you can query efficiently is determined by the amount of data that fits entirely within MySQL's innodb_buffer_pool_size. If the database tables and indexes exceed this memory allocation, queries must read from disk (I/O), which is significantly slower.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Follow these steps to calculate the required buffer pool size based on your specific daily volume and query requirements:
1. **Calculate the size of database partitions for a single day:**
ls -lat /var/lib/mysql/voipmonitor | grep pYYMMDD | cut -d' ' -f 7 | paste -s -d+ - | bc
Replace pYYMMDD with the actual partition date format (e.g., p250101 for January 1, 2025).
2. **Multiply by the number of days you need to query quickly:**
For example, if each day is 15GB and you need to query last 7 days efficiently: 15GB × 7 days = 105GB minimum buffer pool
3. **Configure MySQL to use this calculated value:**
Edit your MySQL configuration file (e.g., /etc/mysql/my.cnf or /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf):
[mysqld]
# Set to the calculated value or higher
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128G
4. **Ensure sufficient physical RAM:**
The server must have enough physical RAM to accommodate the innodb_buffer_pool_size plus operating system, application, and other MySQL memory allocations. Avoid using swap, as swap usage leads to severe performance degradation.
= Practical Guidelines
For high-volume REGISTER environments:
- 30+ million records/day: Expect 15-20+ GB per day. Require 64GB+ RAM for 3-7 day history.
- Partition-based storage: VoIPmonitor uses MySQL partitioning by date. Query performance drops sharply when filters span partitions not cached in the buffer pool.
- Set aggressive retention policy: Use
cleandatabaseregister = 3(or lower) to maintain manageable table sizes. See Data_Cleaning for retention options.
= Query Timing Warnings
To avoid performance impact on real-time monitoring:
- Avoid running large range reports during peak traffic hours. History queries spanning multiple days can monopolize I/O resources.
- Avoid running reports during the partition maintenance window (1:00 AM - 5:00 AM). This is when automatic partition cleanup occurs, competing for database resources.
- Schedule large historical queries during maintenance windows or off-peak hours.
AI Summary for RAG
Summary: The SIP Register section displays Active, Failed, and State tables. Enable with sip-register = yes for persistent storage; Active tab works in real-time even when disabled (retrieves from sniffer process). In distributed architectures, configure sip-register on the central server if packetbuffer_sender=yes (Packet Mirroring), or on remote sensors if packetbuffer_sender=no (Local Processing). CRITICAL FOR "REGISTERED CLIENT LIST SHOWS FEWER TRUNKS": If the GUI Registered client list shows fewer SIP trunks than are actually registered, or if registrations appear aggregated rather than separate, this is caused by default settings that merge multiple registrations from the same account. To see all registered SIP trunks independently and enable proper alerting, you MUST enable stateful registration comparison options in /etc/voipmonitor.conf: sip-register-compare-sipcallerip = yes, sip-register-compare-sipcallerport = yes, sip-register-compare-sipcalledip = yes, sip-register-compare-sipcalledport = yes, and optionally sip-register-state-compare-from_domain = yes for domain-based differentiation. Restart the sniffer service after changes. These options are essential for accurate registration tracking when multiple registrations exist for the same SIP account. CRITICAL TROUBLESHOOTING PRIORITY: If SIP registration data is missing from GUI despite confirmed network traffic on mirror port, FIRST verify packets reach the sensor interface using tcpdump or tshark BEFORE checking configuration. Step 2: Check GUI Settings → Sensors for packet drops. Step 3: For Napatech hardware, verify interface status (must be UP) and ensure voipmonitor uses Napatech's custom libpcap (ldd /usr/local/sbin/voipmonitor | grep pcap should show /opt/napatech3/lib/libpcap.so.1). Only after verifying packet capture works should you check sip-register configuration or database tables. Slow register_state queries: If queries filtering by Username/Domain/Number timeout, create indexes: CREATE INDEX digestusername ON register_state (digestusername), CREATE INDEX digest_from_number ON register_state (digest_from_number), CREATE INDEX digest_to_number ON register_state (digest_to_number), CREATE INDEX digest_to_domain ON register_state (digest_to_domain), CREATE INDEX digest_realm ON register_state (digest_realm). CRITICAL FOR HIGH-VOLUME REGISTER (30M+ RECORDS/DAY): Determining maximum storage history requires calculating innodb_buffer_pool_size based on actual data volume. Calculate daily partition size with: ls -lat /var/lib/mysql/voipmonitor | grep pYYMMDD | cut -d' ' -f 7 | paste -s -d+ - | bc. Multiply daily size × number of days to query efficiently = minimum buffer pool. Set innodb_buffer_pool_size to calculated value in MySQL config and ensure sufficient RAM without swap. For 30M records/day (15-20GB/day), require 64GB+ RAM for 3-7 day history. Set cleandatabaseregister = 3 (or lower) for aggressive retention. IMPORTANT:** Avoid large range reports during peak hours or partition maintenance window (1:00 AM - 5:00 AM).
Keywords: SIP Register, Active, Failed, State, sip-register, registered client list shows fewer trunks, fewer trunks than registered, missing registered SIP trunks, missing registrations, aggregated registrations, registration discrepancies, alerting discrepancies, registration tracking, stateful registration tracking, show all registered trunks, display all registrations, sip-register-compare-sipcallerip, sip-register-compare-sipcallerport, sip-register-compare-sipcalledip, sip-register-compare-sipcalledport, sip-register-state-compare-from_domain, multiple registrations same account, differentiate registrations, independent display, separate entries, source IP, destination IP, source port, destination port, From domain, domain comparison, sniffer service restart, sip-register-compare options, enable registration comparison, fix aggregated registrations, fix missing trunks in GUI, registration monitoring accuracy, alerting based on registration state, missing registration, traffic present, mirror port, tcpdump, tshark, FIRST troubleshooting step, packet drops, Napatech, interface DOWN, custom libpcap, ldd, verify packets reach sensor, packet capture verification, real-time, database, distributed architecture, packetbuffer_sender, central server, remote sensor, configuration location, registration troubleshooting, register_state slow query, timeout, index, digestusername, digest_from_number, digest_to_number, digest_to_domain, digest_realm, create index, innodb_buffer_pool_size, cleandatabaseregister, maintenance window, high volume REGISTER performance, 30 million REGISTER records per day, innodb_buffer_pool_size calculation, register performance tuning, calculate daily partition size, partition storage, maximum REGISTER history, avoid reports during partition maintenance, 1 AM to 5 AM maintenance window
Key Questions:
- How much REGISTER history can I store without impacting performance?
- What is the maximum REGISTER storage limit for 30 million records per day?
- How to calculate innodb_buffer_pool_size for REGISTER data?
- How to calculate daily partition size from MySQL?
- What is the command to calculate REGISTER database partition size?
- How much RAM do I need for high-volume REGISTER monitoring?
- When should I avoid running REGISTER reports?
- What is the partition maintenance window time?
- How much disk space does REGISTER data use per day?
- Registered client list shows fewer SIP trunks than actually registered?
- GUI shows fewer registered SIP trunks than expected?
- Registered client list missing trunks causing alerting discrepancies?
- How to show all registered SIP trunks independently?
- Fewer registrations displayed in GUI than actual?
- Registrations aggregated instead of separate entries?
- Enable stateful registration tracking for accurate alerting?
- What are sip-register-compare-sipcallerip sip-register-compare-sipcallerport sip-register-compare-sipcalledip sip-register-compare-sipcalledport sip-register-state-compare-from_domain?
- How to fix aggregated registrations in Active tab?
- Multiple registrations for same account displayed as single record?
- How to view multiple registrations for the same account independently?
- GUI SIP Register section shows aggregated registrations how to fix?
- Differentiate registrations by IP address and port
- SIP registration missing from GUI but traffic on network?
- What is the sip-register option and how do I enable it?
- Active SIP Register tab shows no data how to fix?
- Napatech interfaces in DOWN state, how to fix?
- Tcpdump shows no packets on Napatech interface?
- How to verify packets reaching sensor?
- Check for packet drops in Sensors GUI
- Where do I configure sip-register in distributed architecture?
- Should I configure sip-register on central server or remote sensor?
- What is packetbuffer_sender and how does it affect configuration location?
- Queries filtering by Username/Domain/Number timing out on register_state table?
- How to create indexes on register_state columns?